- Written By
Sushmita Rout
- Last Modified 16-01-2025
Absolute Zero and Absolute Scale of Temperature
Absolute Zero and Absolute Scale of Temperature: Ever imagined what could be the lowest temperature? Is it possible to attain this temperature? Yes, there exists such temperature. It is \(-273.15\) degrees Celsius on the Celsius scale. It is the coldest possible temperature, and formally, it is the temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. It is the temperature at which the motion of particles in a system ceases to exist. It measures zero on the Kelvin scale of temperature. Let’s explore more about it and its value in different temperature scales.
What is Absolute Zero?
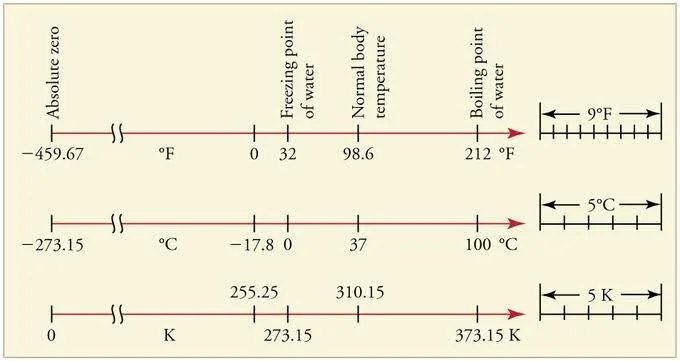
Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature at which a substance retains no heat energy. The fundamental particles of nature have negligible vibrational motion at this temperature. On the Kelvin scale, it is exactly \(0\,{\rm{K}}\), and on the Celsius scale, it is \(–273.15\) degrees Celsius, which is comparable to \(-459.67\) degrees Fahrenheit.
Celsius Scale
Celsius, or centigrade, is the most commonly used unit of measuring temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius \(\left( {1701 – 1744} \right)\).
Water has azing point of \({0^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\), and boiling point at \({100^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\), both at one atmospheric pressure. The following is the relationship between degrees Celsius and Kelvin:
\({{\text{T}}_{{\text{Celsius}}}} = {{\text{T}}_{{\text{Kelvin}}}} – 273.15\)
Fahrenheit Scale
Water has azing point of \(32\) degrees Fahrenheit and a boiling point of \(212\) degrees Fahrenheit on the Fahrenheit scale.
Temperature is measured on the Fahrenheit scale. It is named after physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, which he proposed in \(1724\). The unit of this scale is degree Fahrenheit \(\left( {^{\rm{o}}{\rm{F}}} \right)\).
The boiling andzing points of water are exactly \(180\) degrees apart in the Fahrenheit system. Hence, a degree on the Fahrenheit scale is \(1/180\) of the temperature difference between thezing and boiling points of water. Water’szing and boiling points are \(100\) degrees apart on the Celsius scale. A temperature interval of \(1\) degree Fahrenheit \(\left( {^{\rm{o}}{\rm{F}}} \right)\) is equivalent to a temperature interval of \(5/9\) degrees Celsius \(\left( {^{\rm{o}}{\rm{C}}} \right)\). To convert \({^{\rm{o}}{\rm{F}}}\) to \({^{\rm{o}}{\rm{F}}}\), you can use the following formula:
\(\frac{{^{\rm{o}}{\rm{C}}}}{5} = \frac{{^{\rm{o}}{\rm{F}} – 32}}{9}\)
The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales intersect at \( – {40^{\rm{o}}}\) (\( – 40{{\rm{ }}^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{F}}\) and \( – 40{{\rm{ }}^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\) represent the same temperature). Absolute zero (\( – 273.15{{\rm{ }}^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\), or \(0\,{\rm{K}}\)) is defined as \( – 459.67{{\rm{ }}^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{F}}\).
Know About Temperature Conversion Formula Here
Kelvin Scale
The kelvin is a temperature measurement unit; the null point of the Kelvin scale is absolute zero, the coldest temperature imaginable. It has the unit symbol \({\rm{K}}\) and is one of the seven base units of the International System of Units \(\left( {{\rm{SI}}} \right)\). The Kelvin scale is a thermodynamic, absolute temperature scale with absolute zero as the null point. Absolute zero is the temperature at which all thermal motion ends in the classical thermodynamics model.
The following formula is used to convert kelvin to degrees Celsius:
\({{\text{T}}_{{\text{Celsius}}}} = {{\text{T}}_{{\text{Kelvin}}}} – 273.15\)
Absolute Scale of Temperature
The absolute temperature scale is a thermometric scale on which a reading of zero coincides with the theoretical absolute zero of temperature—i.e., the thermodynamic equilibrium state of minimum energy.
Summary of Absolute Zero and Absolute Scale of Temperature
The coldest temperature imaginable is \(-273.15\) degrees Celsius. This measures \(0\) on the Kelvin scale. This temperature is also known as absolute temperature. It measures \(-459.67\) degrees on the Fahrenheit scale, and at this temperature, the fundamental particles of nature have minimal vibrational motion. This page explains the concept of absolute temperatures and different temperature scales. It also explains the conversion formulas from which a temperature reading on a particular scale can be converted into the other.
FAQs on Absolute Zero and Absolute Scale of Temperature
Q.1. Why is 0 Kelvin known as absolute zero?
Ans: At \(0\) Kelvin, all the atoms have been completely stopped relative to each other, hence is known as “absolute zero” and corresponds to the number zero on the Kelvin temperature scale.
Q.2. What is absolute zero, and what temperature is it in Kelvin?
Ans: Absolute zero, often known as zero kelvins, is a temperature of \(-273.15\) degrees Celsius (\(-459.67\) degrees Fahrenheit) that indicates a point on a thermometer where a system has reached its lowest potential energy or thermal motion.
Q.3. What is the difference between absolute and relative temperature scales?
Ans: Temperature values on an absolute scale do not have degree symbols. Celsius and Fahrenheit are relative scales based on thezing point of water, so they use degree symbols.
Q.4. Which scale is known as the thermodynamic scale of temperature?
Ans: The Kelvin temperature scale is also known as the thermodynamic scale of temperature.
Q.5. What is the difference between degrees Celsius and centigrade?
Ans: The Celsius temperature scale is the most commonly used temperature scale in the world and the simplest to understand. Celsius is known by the traditional name of centigrade. Water has azing point of \(0\) degrees Celsius and a boiling point of \(100\) degrees Celsius. \(^{\rm{o}}{\rm{C}}\) is the abbreviation for Celsius.
We hope this article on Absolute Zero and Absolute Scale of Temperature has helped you. If you have any queries, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you.