- Written By
Sushmita Rout
- Last Modified 29-01-2025
Barium Hydroxide Formula: Definition, Molar Mass, IUPAC ID, MCQs
Barium Hydroxide Formula: Did you know Baryta or Baryta water is chemically known as Barium hydroxide? It is white and granular and one of the principal compounds of Barium. Let’s learn everything about the chemical compound barium hydroxide and its chemical formula in detail.
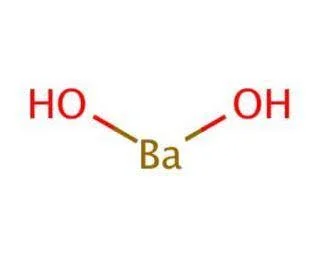
The chemical formula of Barium Hydroxide is \({\rm{Ba(OH)}}_2\). It is available in \(3\) forms – Anhydrous, Monohydrate, and Octahydrate. The structure of barium hydroxide consists of \(2\) hydroxyl anions \(({\rm{OH}}^-)\) and one barium cation \(({\rm{Ba}}^{2+})\).
Preparation of Barium Hydroxide
Barium hydroxide is produced by the reaction of barium oxide \(({\rm{BaO}})\) with the water \(({\rm{H}}_2 {\rm{O}})\).
\({\text{BaO}} + 9{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {\text{Ba}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_2} \cdot 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\).
Study About Alkaline Earth Metals Here
Physical Properties of Barium Hydroxide
The physical properties of barium hydroxide are given below:
- Barium hydroxide is an odourless, poisonous, white coloured solid.
- The molar mass of Barium Hydroxide is \(171.34\;{\rm{g/mol}}\).
- The melting point of Barium Hydroxide varies depending on how much water is present. At \(78\) degrees Celsius, the octahydrate phase melts. The monohydrate phase melts at \(300\) degrees Celsius, while the anhydrous form melts at \(407\) degrees Celsius.
- All three forms are partially soluble with water at low temperatures. However, the solubility of barium hydroxide in water increases with the increase in temperature.
- Barium hydroxide has a density of \(3.743\;{\rm{g/mL}}\) (in monohydrate form) and \(2.18\;{\rm{g/mL}}\) (in octahydrate form).
- Barium Hydroxide boils at \(780\) degrees Celsius and decomposes into Barium oxide at a temperature above \(800\) degrees Celsius.
Chemical Properties of Barium Hydroxide
The chemical properties of barium hydroxide are explained below:
- Barium hydroxide is ionic in nature, i.e., in an aqueous solution, it can furnish two hydroxide or hydroxyl ions/molecule.
- If it is hydrated, then one or eight water molecules will be in the surrounding of the cations and the anions.
- Barium hydroxide on dissolution produces alkali solutions. This happens due to the release of hydroxyl anions. Hence, it undergoes neutralization reactions with acids.
- It undergoes a neutralization reaction with sulphuric and phosphoric acids to form useful barium salts such as barium sulphate and barium phosphate.
- When heated above \(800^\circ {\rm{C}}\), Barium hydroxide decomposes into barium oxide.
- Barium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form barium carbonate whereas, hydrogen sulphide it forms barium sulphide.
- A double replacement reaction forms many insoluble or less soluble barium salts when the barium hydroxide aqueous solution is mixed with other metal salts.
- An endothermic reaction takes place when barium hydroxide reacts with ammonium salts.
Uses of Barium Hydroxide
The uses of barium hydroxide are explained below:
- It is used as a source of Barium to produce certain barium salts such as barium phosphate, barium sulfide, and barium sulfate.
- It is also used in the analytical standard for the titration of weak acids.
- It is used in the manufacture of glass, oil, alkalis and grease additives, barium soaps, and other barium compounds.
Health Risks of Barium Hydroxide
The health risks of barium hydroxide are explained below:
- Inhalation of barium dust can cause respiratory tract irritation and may produce benign pneumoconiosis known as baritosis.
- Barium ions are toxic to muscles and may cause paralysis.
- It is an extremely dangerous neurotoxin that has adverse effects on the heart and the central nervous system (CNS).
Barium hydroxide is one of the primary compounds of Barium. It is a precursor to the synthesis of many barium salts. Its reaction with ammonium chloride is an important endothermic reaction. In this article, we learned the chemical formula, structure, properties, and uses of Barium hydroxide.
Barium Hydroxide Formula MCQs
- Barium hydroxide is a:
- Monoacidic base
- Diacidic base
- Triacidic base
- Both A and B
Correct answer: B
Hint: Barium hydroxide on dissolution furnishes two hydroxyl ions.
- The van’t Hoff factor (i) for a dilute aqueous solution of barium hydroxide solution is:
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
Correct answer: D
Hint: Barium hydroxide dissociates to form Barium cation and hydroxyl anion.
- What type of reaction takes place when Barium hydroxide is mixed with ammonium chloride?
- Exothermic
- Endothermic
- Combination
- None of these
Correct answer: B
Hint: The reaction absorbs the heat of the surrounding.
- Barium hydroxide is a-
- Strong acid
- Strong base
- Weak acid
- Weak base
Correct answer: B
Hint: It has same nature as NaOH, KOH.
- Barium hydroxide is also available as?
- Dihydrate
- Trihydrate
- Octahydrate
- None of these
Correct answer: C
Hint: Its chemical formula is Ba(OH)2.8H2O
- Which of the following compound is produced when Barium hydroxide is heated above 800℃?
- Barium phosphate
- Barium sulfide
- Barium sulfate
- Barium Oxide
Correct answer: D
Hint: It is also known as Calcined baryta.
- With Sulphuric acid, barium hydroxide undergoes which type of reaction?
- Neutalisation reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Addition reaction
- Combination reaction
Correct answer: A
Hint: This reaction takes place between an acid and a base.
- The molar mass of Barium hydroxide Octahydrate is:
- 315.46 g/mol
- 320.46 g/mol
- 325 g/mol
- 330 g/mol
Correct answer: A
Hint: The chemical formula of Barium hydroxide Octahydrate is Ba(OH)2.8H2O.
- What does the number 2 in the Barium hydroxide formula signify?
- Hydroxyl is a monoatomic anion
- Barium is an alkali metal
- Barium belongs to group 2 of the Periodic Table
- Barium is a poisonous gas.
Correct answer: C
Hint: Barium is an alkaline earth metal.
- 25 mL of a solution of barium hydroxide on titration with a 0.1 molar solution of hydrochloric acid gave a titre value of 35 mL. The molarity of barium hydroxide solution is-
- 0.07
- 0.14
- 0.28
- 0.35
Correct answer: AHint: Use the formula N1V1 = N2V2
Q.1. What is the formula for barium hydroxide?
Ans: The chemical formula of Barium Hydroxide is \({\rm{Ba(OH)}}_2\). It is available in \(3\) forms – Anhydrous, Monohydrate, and Octahydrate. The structure of barium hydroxide consists of \(2\) hydroxyl anions \(({\rm{OH}}^-)\) and one barium cation \(({\rm{Ba}}^{2+})\).
Q.2. Why is there a \(2\) in barium hydroxide formula?
Ans: Barium belongs to the group of alkaline earth metals. These elements can lose two outermost electrons to attain the noble gas configuration. A charge of \(+2\) is available on these metals. Hydroxide is a negative polyatomic ion with a value of \(1\), and \(-1\) is the charge. They exchange their charges to form an ionic compound \({\rm{Ba(OH)}}_2\).
Q.3. Is Barium Hydroxide a base or an acid?
Ans: Barium Hydroxide, like \({\rm{NaOH}}\) and \({\rm{KOH}}\), is a stable base. Barium Hydroxide is a metal hydroxide of group IIA that dissolves in water to produce hydroxyl ions.
Q.4. What is the charge on \({\rm{Ba(OH)}}_2\)?
Ans: Barium is an atom that belongs to Group \(2\) of the Modern Periodic Table, so it has two valence electrons, and its charge is \(+2\). Hydroxide is a negative polyatomic ion with a value of \(1\), and \(-1\) is the charge. They mix to form an ionic compound with no overall charge.
Q.5. What happens when barium hydroxide is heated?
Ans: When heated above \(800^\circ {\rm{C}}\), Barium hydroxide decomposes into barium oxide.
Q.6. What happens when Barium hydroxide is mixed with ammonium chloride?
Ans: When Barium hydroxide is mixed with ammonium chloride, an endothermic reaction takes place. Ammonium Chloride is slightly acidic, whereas Barium Hydroxide is a strong base. This acid-base reaction will result in the formation of Barium chloride, ammonia, and water.
\({\text{Ba}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_2} + 2{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{Cl}} \to {\text{BaC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + 2{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\).
Study About Simple Oxides Here
We hope this article on the barium hydroxide formula is helpful to you. If you have any questions related to this page, reach us through the comment box below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.