- Written By
Priyanka Srivastava
- Last Modified 20-01-2025
Bioremediation: Definition, Conditions, & Advantages
Bioremediation: Although most of us now live in urban areas, everyone likes to be in a clean, green place like in rural areas. Urban areas have gone dirty with many toxic pollutants. However, sometimes conventional methods to clean pollutants do not work. Bioremediation is a good option to clean up the environment in which microbes or plants are used.
Bioremediation cleans up the environment naturally without the use of toxic chemicals. So, it is an environmentally friendly method. In this article, we will discuss about bioremediation in detail. Scroll down to find more!
Bioremediation is a unique technique for cleaning the environment. In this technique, microbes or plants are used to detoxify the contaminants in the soil, water, and other environments.
The features of bioremediation are as follows:
- It is the process of removing or breaking down pollutants from contaminated sites using organisms.
- Biological agents like bacteria, fungi, and plants are used to remove pollutants from contaminated sites.
- This process is applicable to oil spills, contaminated soils, underground water, underground pipe leaks, and even crime scene cleanups, etc.
- Microbes eat the wastes as food, like hydrocarbons of oil.
- Microorganisms release enzymes to metabolize toxic compounds of the contaminants to water and harmless gases like CO2.
- It involves oxidation-reduction reactions in most of the bioremediation processes.
- This process helps in reducing the impact of industrialization and agricultural processes.
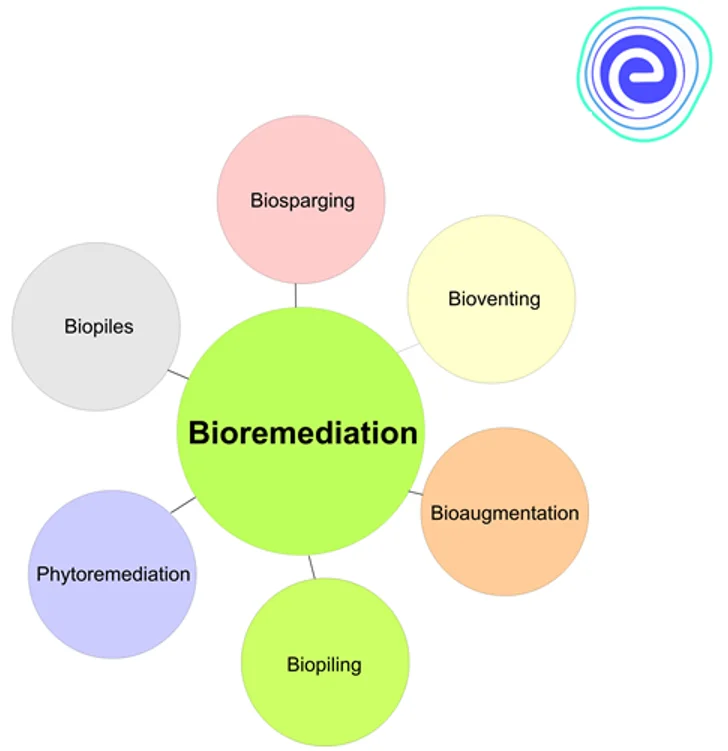
On the basis of treatment locality, bioremediation can be classified as:
- Ex-situ Bioremediation
- In-situ Bioremediation
1. Ex-situ Bioremediation
Ex-situ bioremediation: It means treating the contaminants away from the site. Like contaminated soil or water is pumped from where it is found and taken to somewhere else like in industries for bioremediation and then put back. Examples of ex-situ bioremediation are- Landfarming, composting, and biopile.
Landfarming
- 1. It is done for soil and sediments which are excavated from their site and is spread to some other area where it has to be treated.
- 2. Here nothing is added from outside. Here we depend on indigenous flora.
- 3. The only thing that has to be done is tilling the soil periodically to provide more and more oxygen to the aerobic bacteria found there to degrade the pollutants aerobically.
Composting
Contaminated soil is first excavated and is mixed with some organic material like manure or agricultural wastes, and then degradation is allowed to happen.
Biopile
1. This method is a hybrid of both landfarming and composting. The only difference is that volatilization and leaching of water are controlled.
2. In this method, contaminated surface soil is excavated and not deep soil.
3. Organic materials like manures or agricultural wastes are added, and a proper aeration system is piled with the excavated soil to enhance the aerobic degradation process by the aerobic microbes.
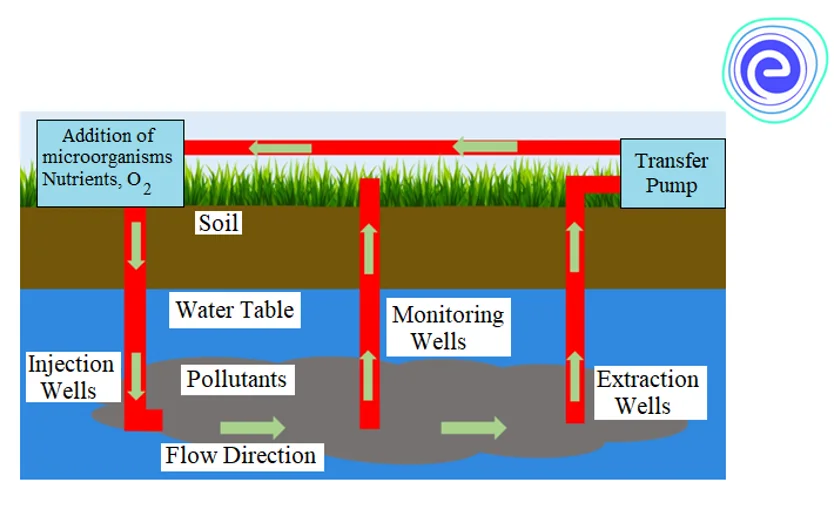
2. In-situ Bioremediation
It means treating the contaminants on the site.
Fig: In-situ bioremediation
Natural Attenuation
- 1. It occurs without human interference.
- 2. Here we depend upon natural or indigenous flora of microorganisms to do their job of cleaning up by degradation process.
- 3. We do not add anything there like any flora or any microorganism.
- 4. Only monitoring is done periodically.
Bioventing
- 1. It is a common method.
- 2. It is used where contamination is deep inside the soil.
- 3. In this method, there are wells or channels, or tunnels that are dug into the soil.
- 4. Through these wells, air and nutrients are supplied.
- 5. Here we depend upon the indigenous flora of the microorganisms that are already present there. So, these microbes get stimulated with the supply of fresh air and nutrients, and the process of biodegradation starts immediately.
- 6. Airflow pressure is kept low so that volatilization of contaminants does not occur in the atmosphere and thus prevents air pollution.
Biosparging
- 1. This process is generally involved with the cleaning of contamination of groundwater, the saturated contaminated zones.
- 2. In this method also, wells and tunnels are made to supply nutrients and oxygen to the contaminants. So, that indigenous bacteria gets activated, and the biodegradation process starts at a faster rate.
- 3. Here wells are attached to vacuum pumps and compressor pumps.
- 4. This method is similar to the bioventing method, but here the pressure with which nutrients and fresh air are supplied is high.
Bioaugmentation
- 1. In this process, microbes are added in addition to the nutrients and oxygen to the area where contaminants have to be degraded.
- 2. Here genetically engineered microbes having high degradation abilities are added.
Fig: Different types of Bioremediation
For the efficiency of the bioremediation process, the right amount of different physical and chemical conditions are required. These are:
- 1. pH
- 2. Temperature
- 3. Nutritional requirements
- 4. Toxicity of contaminants
- 5. Microbe energy source
The advantages of bioremediation are as follows:
- This method is eco-friendly. It occurs naturally and causes less or no damage to the environment as much of its processes to occur underground.
- Contaminants are converted into water and harmless gases.
- It is cost-effective as extensive equipment and labor are not needed.
- It is a permanent solution as the degraded material cannot revert back to the previous one.
- It is a recommended method for removing oil stains.
The disadvantages of bioremediation are as follows:
- It takes a large area and time from months to years.
- It is limited to the compounds which are degradable because every compound in this biosphere is not degradable.
- It is not able to remove all kinds of impurities from the contaminated site. Like, some kind of inorganic contaminants cannot be treated with this bioremediation method.
- Hard to measure and see the results.
- Introduced microbes may or may not flourish in the newly given environment.
- Less predictable than conventional techniques.
- Some heavy metals cannot be completely broken down, resulting in toxic by-products.
The applications of bioremediation are as follows:
- It is used to clean groundwater and soil.
- It is used for the remediation of metals, pesticides, volatile organic compounds, etc., from the contaminated sites.
- Different plants like Indian mustard, sunflower plant, etc., are used for removing metals from soil.
On the basis of organisms used in the bioremediation process, it is of the following three types:-
1. Mycoremediation– It is the process of bioremediation in which fungus is used to clean up the contaminants.
2. Phytoremediation– It is the process of bioremediation in which plants are used for converting toxic substances to non-toxic ones. Some plants take in contaminants like metals with water and nutrients from the soil to its body through roots. At the same time, some plants supply nutrients to the microbes present in the soil to enhance biodegradation activity. Examples of plants used in phytoremediation are water hyacinth, Indian mustard, Sunflower, etc.
From the above discussion, we can conclude that bioremediation is the environmentally friendly approach to clean up the toxicity of the soil, water, etc. It allows naturally occurring organisms, i.e., microbes or plants, to degrade toxic compounds. Advanced technologies have made bioremediation one of the most developing methods to restore the environment. Ex-situ and in-situ methods of bioremediation are executed. Ex-situ methods are landfarming, composting, and biopiles, while in-situ methods are bioventing, biosparging, bioaugmentation. Right pH, temperature, and nutrients are required for the proper working of the microbes in this method.
Q.1. What are 2 types of bioremediation?
Ans: Ex-situ and In-situ methods of bioremediation are the two types of bioremediation. Ex-situ methods involve landfarming, composting, and biopiles, while in-situ methods are bioventing, biosparging, bioaugmentation.
Q.2. How safe is bioremediation?
Ans: Bioremediation is an environmentally-friendly method. In this method, contaminants are converted into water and harmless gases like \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\).
Q.3. How do microorganisms help in bioremediation?
Ans: Microorganisms release enzymes to metabolize toxic compounds of the contaminants to water and harmless gases like \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\).
Q.4. What is bioremediation in simple words?
Ans: Bioremediation is a unique technique of cleaning the environment. In this technique, microbes or plants are used to detoxify the contaminants in the soil, water, and other environments.
Q.5. What is Bioaugmentation in bioremediation?
Ans: In this process, microbes are added in addition to the nutrients and oxygen to the area where contaminants have to be degraded. Here genetically engineered microbes having high degradation abilities are added.
Learn About Career in Biotechnology
Now that you have a detailed article on Bioremediation, we hope you study well. If you get stuck somewhere do let us know in the comments sections. We will get back to you at the earliest.