- Written By
Ankita Sahay
- Last Modified 31-12-2024
Conditions for Chemical Reaction
Conditions for Chemical Reactions: Chemical reactions occur everywhere and all the time on Earth and in the Universe, but it requires certain conditions. For example, combustion can only happen when there is enough heat, enough oxygen and fuel. A chemical reaction involves the interaction of different atoms, molecules, substances, or matter. These interactions can be triggered by energy. The energy involved can come in many forms, such as light, heat, or pressure. In a chemical reaction, the atoms or molecules that interact with each other are known as reactants, and the atoms or molecules produced by the reaction are known as products.
Some necessary conditions required for a chemical reaction to occur are: firstly, the proper collision of reactants molecules or atoms to break and make the bonds that leads to the formation of new products, and secondly, the presence of a sufficient amount of energy in the form of heat, light, etc. Based on the path followed in a chemical reaction and the type of products formed, chemical reactions are distinguished into different types like combination reaction, decomposition reaction, displacement reaction, double-displacement reaction, combustion reaction, precipitation reaction, etc. They are classified as exothermic and endothermic reactions based on the energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
What is a Chemical Reaction?
The reaction in which one chemical substance (reactant) transforms into another new chemical substance (product) is called a chemical reaction. A chemical change leads to the formation of new substances, whereas a physical change leads to a change in colour or state and no new substances are formed.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Based on the formation of different types of products or changes in the condition of reactants, the chemical reactions are classified into different types:
Learn Everything About Types Of Equilibrium Here
- Combustion reaction
- Neutralisation reaction
- Combination reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Redox Reaction
- Double-Displacement Reaction or Precipitation
1. Combustion Reaction
A type of chemical reaction between a fuel and oxygen that produces a product that burns to produce carbon dioxide, water and evolves heat. For example:
\({\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{(g) + 2}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + 2}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O(g) + Heat}}\)
2. Neutralisation Reaction
A reaction between an acid and a base to produce salt and water as the products is known as a neutralisation reaction. The pH of the product formed is \(7\). For example, a neutralisation reaction occurs between Hydrochloric acid \(({\rm{HCl}})\) and Sodium Hydroxide \(({\rm{NaOH}})\) to form sodium chloride and water.
\({\rm{HCl + NaOH}} \to {\rm{NaCl + }}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\)
3. Combination Reaction
It is a type of chemical reaction in which the reactants combine to form a single product. For example:
\({\rm{2Na + C}}{{\rm{l}}_2} \to 2{\rm{NaCl}}\)
4. Decomposition Reaction
A single component breaks down into two or simpler products in a decomposition reaction. A certain amount of energy in the form of heat, electricity, light etc., is required to break the bonds between reactants. For example:
\({\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\left( {\text{s}} \right)\xrightarrow{{{\text{heat}}}}{\text{CaO}}\left( {\text{s}} \right) + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}\left( {\text{g}} \right)\)
5. Redox Reaction
A reaction in which reduction (gain of the electron) and oxidation (loss of electron) take place simultaneously is known as a redox reaction. For example:
\({\rm{Zn}} + 2{{\rm{H}}^ + } \to {\rm{Z}}{{\rm{n}}^{2 + }} + {{\rm{H}}_2}\)
6. Single Displacement Reaction
In this type of reaction, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt. For example, potassium displaces magnesium from its salt magnesium chloride because potassium is more reactive than magnesium.
\(2{\rm{K}} + {\rm{MgC}}{{\rm{l}}_2} \to 2{\rm{KCl + Mg}}\)
7. Double-Displacement Reaction
It is a kind of displacement reaction in which two chemical species react and exchange their ions, i.e., cations and anions, to form two new products. For example:
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}_2}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_4} + {\rm{BaC}}{{\rm{l}}_2} \to {\rm{BaS}}{{\rm{O}}_4} + 2{\rm{NaCl}}\)
Conditions for Chemical Reaction to Occur
Requirement of Heat
Most of the chemical reactions need a source of heat to take place. We call these reactions endothermic reactions as they absorb heat. Most endothermic reactions cannot take place at normal room temperature, so they need external heat. In the laboratories, scientists heat reactants using Bunsen burners. A combustion reaction is one of the most evident types of reaction that requires heat, such as the burning of wood. Other reactions include our daily activities and processes like cooking, boiling, etc.
An example of a decomposition reaction requiring heat is the breakdown of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Dependence of Reaction Rate with Temperature
The speed at which reactants become products is known as the chemical reaction rate. As we know, heat speeds up the reaction rate as it affects the molecules by moving them faster. The faster the molecules will move, the easier it will be for the reaction to take place.
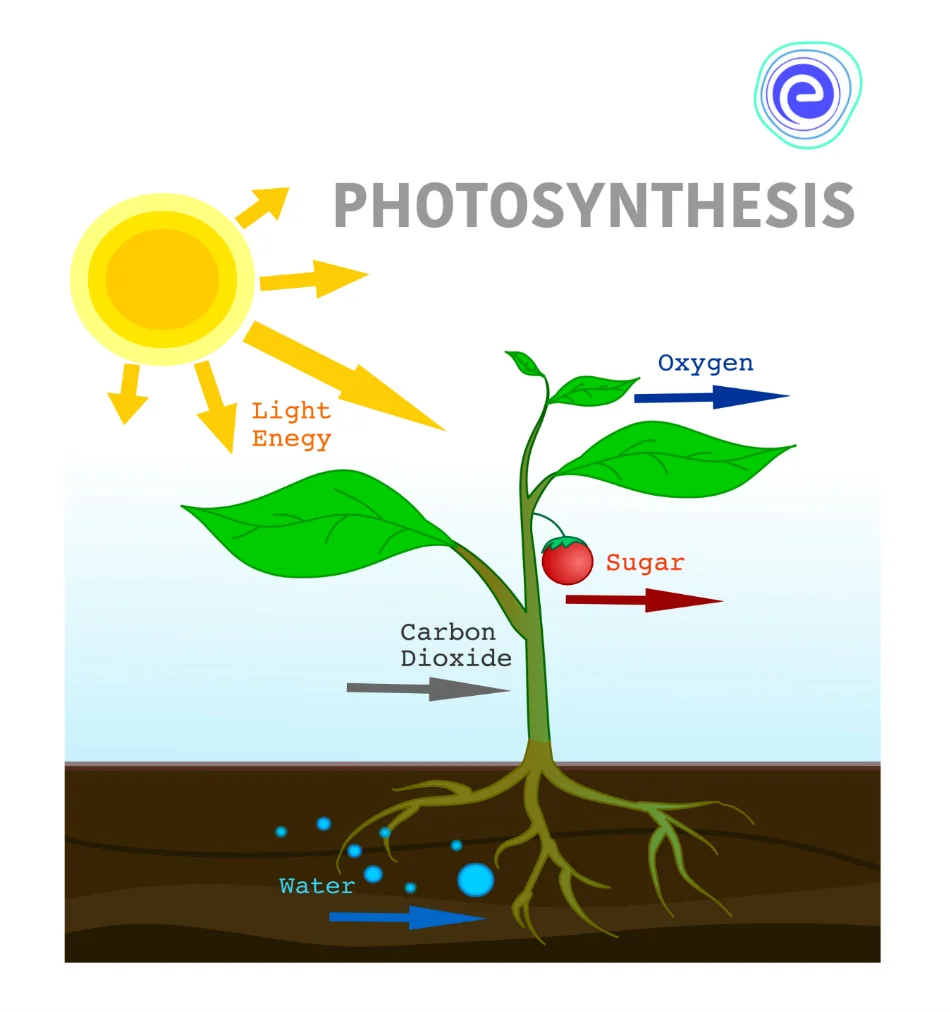
Requirement of Light in Chemical Reactions
Light is another form of energy that is very useful in carrying out chemical reactions; such reactions that take place in the presence of light are known as photochemical reactions. One of the classic examples of a chemical reaction in the presence of light energy is photosynthesis. In this chemical reaction, plants absorb sunlight and allow carbon dioxide and water to react to form glucose and oxygen. Glucose is a type of sugar (food) that plants use for producing their own energy.
Six molecules of carbon dioxide react with six molecules of water during photosynthesis to form one molecule of glucose (a sugar) and six molecules of oxygen in the presence of sunlight.
Some other examples of such photochemical reactions are:
Decomposition of silver bromide into silver and bromine molecules in the presence of light.
\(2{\rm{AgBr}} \to {\rm{2Ag + B}}{{\rm{r}}^2}\)
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of light is another example of such reaction. Hydrogen peroxide is used as a cleaner and disinfectant; due to its reactivity towards the light, hydrogen peroxide mostly comes in an opaque brown bottle.
\(2{{\rm{H}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_2} \to 2{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O}} + {{\rm{O}}_2}\)
Requirement of Pressure in Chemical Reactions
As the temperature affects a chemical reaction, similarly, pressure also affects a chemical reaction. The reason behind this is that the more molecules get compressed, the closer together they come to each other, and as a result, they have more chances of reacting with one another.
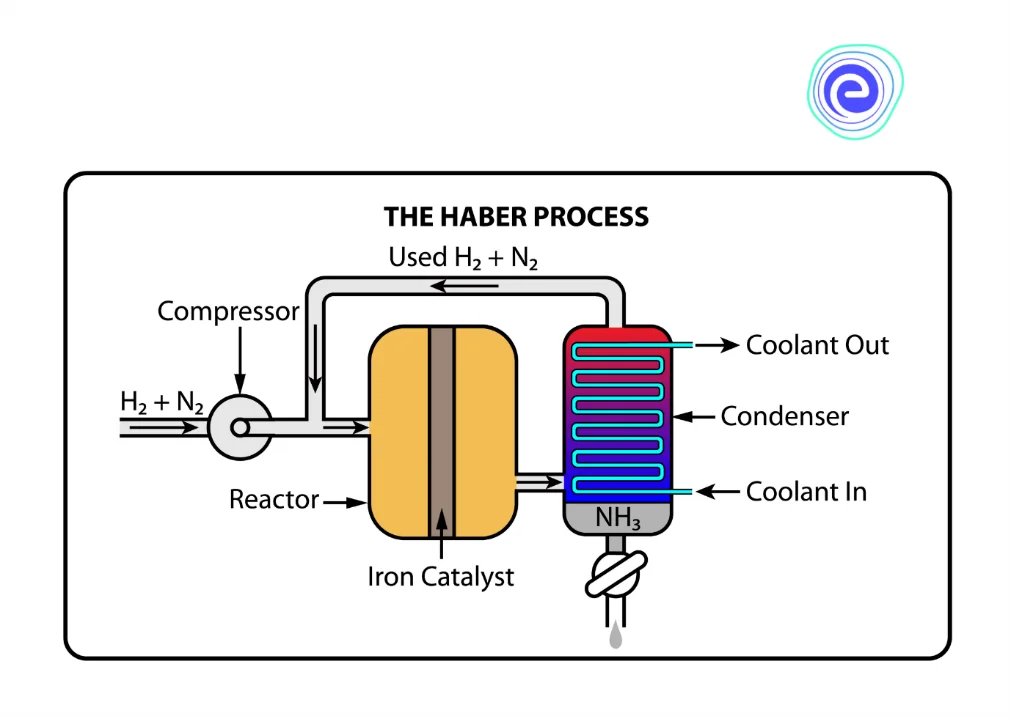
Preparation of Ammonia by Haber’s process requires an increase in pressure to trigger the reaction. The following steps are followed in this process:
- Nitrogen combines with hydrogen in gaseous form to form ammonia.
- This step in the reaction requires both high temperature and high pressure of about \(200\,{\rm{atm}}\)
- It is a reversible reaction
- Under high pressure, the molecules come closer to each other, favouring the forward reaction, which results in the formation of ammonia.
Chemical Reactions Requiring Electric Current
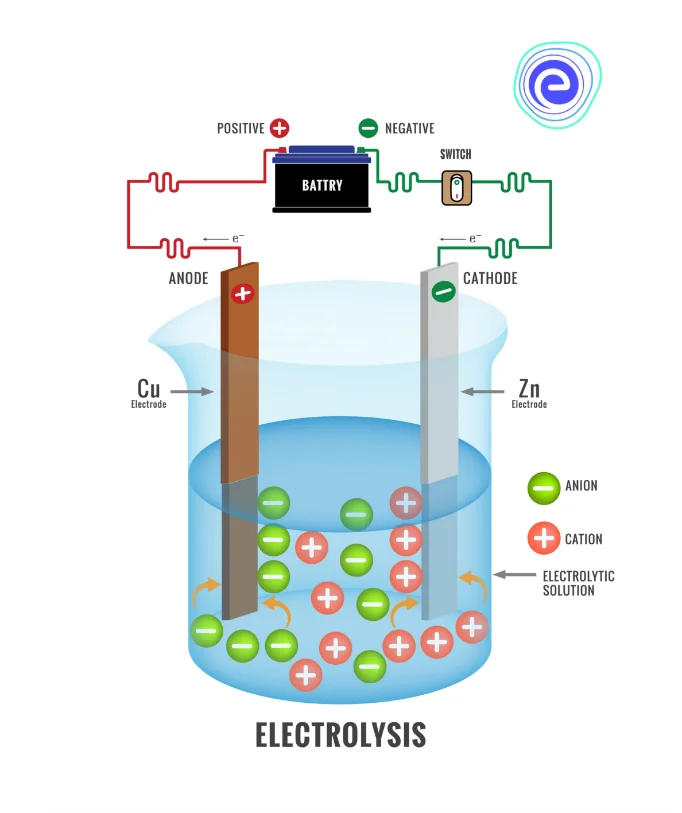
In a special type of chemical reaction known as electrolysis, electricity is used to break the bonds that hold the molecules together. The most popular chemical reaction that takes place in the presence of electricity is the electrolysis of water.
In this process, two pieces of metal called electrodes are connected to the battery. Electrodes are of two types:
- The positive electrode is known as an anode.
- The negative electrode is known as a cathode.
These electrodes are placed in water, and this completes the circuit.
Water molecules split to form oxygen gas, hydrogen ions and electrons at the anode. This type of reaction is known as an oxidation reaction.
\({\rm{2}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O(l)}} \to {{\rm{O}}_2}({\rm{g}}) + 4{{\rm{H}}^ + }({\rm{aq}})\, + 4{{\rm{e}}^ – }\)
At the cathode, hydrogen ions combine with electrons to form hydrogen gas. This is a reduction reaction.
\(4{{\rm{H}}^ + }({\rm{aq}}) + 2{{\rm{e}}^ – } \to {{\rm{H}}_2}({\rm{g}})\)
Another common reaction that involves electricity is the electroplating of zinc on copper. In this process, a thin layer of zinc is applied over another layer of copper in the presence of an electric current.
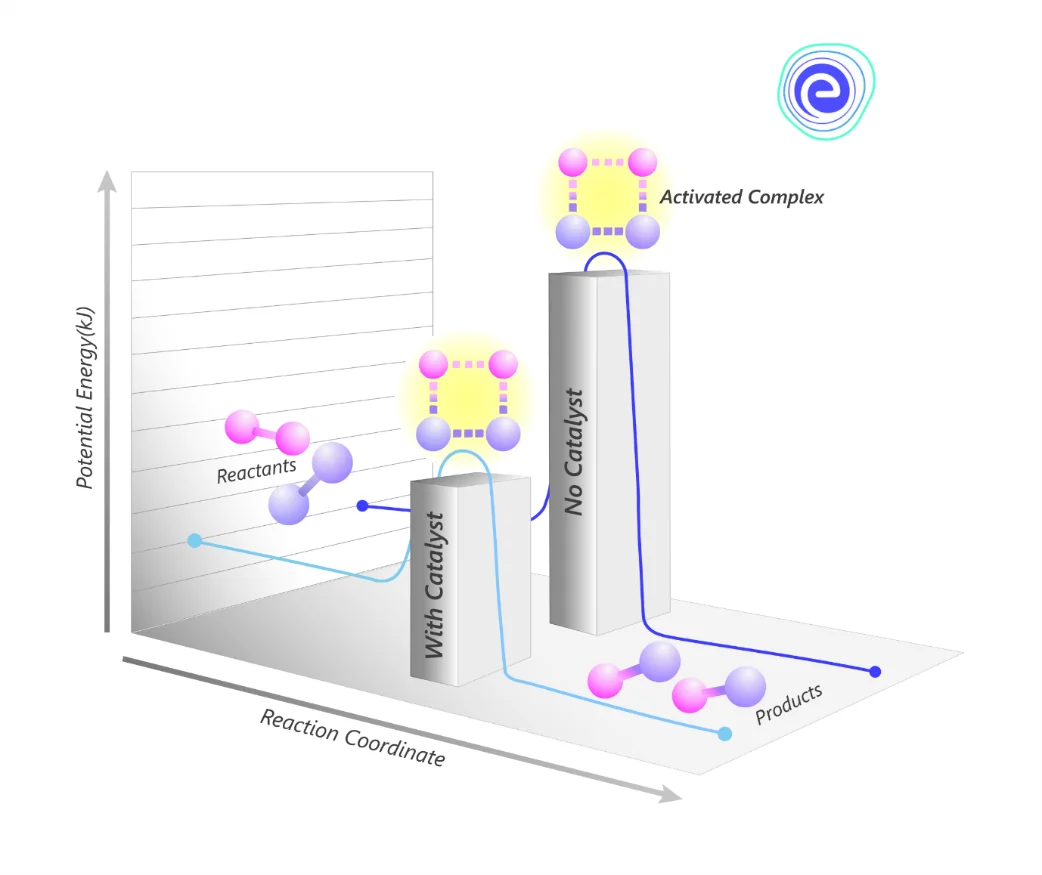
Chemical Reactions Requiring Catalyst
Catalysts are chemical substances that help to complete a reaction by increasing its rate without being used up in the reaction itself. They work by reducing the activation energy required for the reaction to take place.
As catalysts make the reaction happen faster, they are important in many industrial processes. This principle is used in the catalytic converter, which helps to keep toxic air pollution from coming out of vehicles.
Enzymes are biocatalysts that speed up all kinds of biochemical reactions in our bodies. This includes respiration that helps to use oxygen for our growth.
Summary
A reaction in which one chemical substance (reactant) transforms into another new chemical substance (product) is called a chemical reaction. Based on the path followed in a chemical reaction and the type of products formed, chemical reactions are distinguished into different types like combination reaction, decomposition reaction, displacement reaction, double-displacement reaction, combustion reaction, precipitation reaction, etc. This leads to the formation of new substances. All chemical reactions need optimum conditions to take place, such as Most of the chemical reactions need heat to take place. Such reactions are called endothermic reactions as they absorb heat. Such reactions cannot take place at normal room temperature, so they need external heat. Light is another form of energy that is very useful in chemical reactions, such reactions that occur in the presence of light are known as photochemical reactions. Chemical reactions also occur in high pressure as molecules come closer and react with each other. Certain electrochemical reactions take place in the presence of electric current also. Thus, we have learnt that certain conditions are required for a successful chemical reaction.
Q.1. What are the conditions required for a chemical reaction?
Ans: Different conditions required for chemical reaction are:
(i) Heat – Most of the chemical reactions need heat to take place. Such reactions are called endothermic reactions as they absorb heat. Such reactions cannot take place at normal room temperature, so they need external heat.
(ii) Light – Light is another form of energy that is very useful in chemical reactions, such reactions that take place in the presence of light are known as photochemical reactions.
(iii) Pressure – Chemical reactions also occur in high pressure as molecules come closer and react with each other.
(iv) Electricity – Certain electrochemical reactions take place in the presence of electric current also.
Q.2. What are the five characteristics of a chemical reaction?
Ans: Five characteristics of a chemical reaction are:
(i) Conservation of mass,
(ii) Change of state,
(iii) Colour change of reactants,
(iv) Release of gases in some reactions as by-products, and
(v) Change in temperature.
Q.3. What are the factors that affect chemical equilibrium?
Ans: The various factors that affect chemical equilibrium are pressure, volume, and temperature. According to Boyle’s law, the pressure is directly proportional to the volume. Thus, a change in pressure occurs due to the volume change. Temperature affects the chemical equilibrium as in an exothermic reaction; when the temperature increases, the equilibrium constant goes on decreasing, and in the case of an endothermic reaction, the equilibrium constant increases and the temperature increases.
Q.4. What are the different types of chemical reactions?
Ans: The different chemical reactions are combination reaction, decomposition reaction, displacement reaction, double-displacement reaction, combustion reaction, precipitation reaction, etc.
Q.5. How does a catalyst affect the chemical reaction?
Ans: Catalysts are chemical substances that help complete a reaction by increasing its rate without being used up in the reaction itself. They increase the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the activation energy required for the reaction.
Learn About Chemical Reactions And Equations Here
We hope this article on Conditions for Chemical Reaction has helped you. If you have any queries, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you.