- Written By
Sushmita Rout
- Last Modified 03-02-2025
Isomerism in Ethers: Overview, Classification, Examples & FAQs
Isomerism in Ethers: All those compounds that bear the same molecular formula but differ in chemical properties are known as isomers. Isomerism arises from the fact that the atoms in a molecular formula can be organised in multiple ways to produce compounds with varied physical and chemical properties, known as isomers. In alcohols, the atoms that are bonded to the oxygen atom involves hydrogen and carbon.
When the hydrogen atom is replaced by another set of carbon atoms, then alcohols result in isomeric structures known as ethers. For example, dimethyl ether is isomeric with ethanol, and methyl ethyl ether is isomeric with propanol. Let’s understand how the ethers exhibit different isomerism.
Definition of Ethers
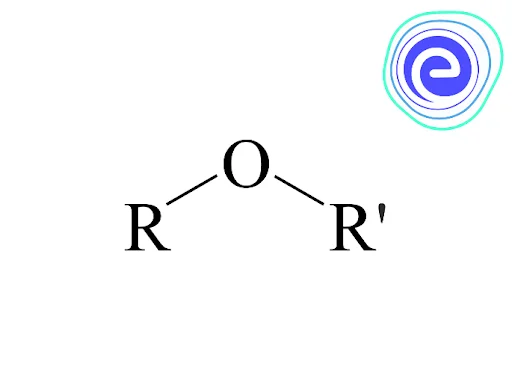
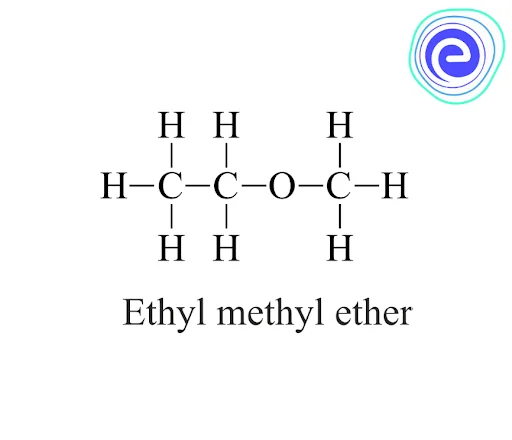
Ethers are a type of organic molecule in which two hydrocarbon groups (alkyl or aryl) are linked together by a single oxygen atom. It is represented by the general formula \({\rm{R – O – R}}\)’ as shown below.
The \({\text{R}}\),’ i.e. the hydrocarbon group in the formula, can be the same as \({\text{R}}\) or different.
Ethers are also obtained when the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group in alcohols is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. For example-
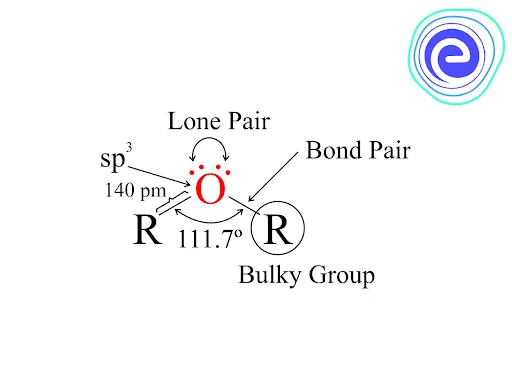
The oxygen and carbon in the \({\rm{C – O – C}}\) bond is \({\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\) hybridised. The bent shape is caused by the repulsion of two lone pairs \({\rm{(lp)}}\) on the oxygen atom. A steric hindrance is created by the presence of bulky groups at both ends of the oxygen atom. The bp-bp repulsion results in a \({\rm{C – O – C}}\) bond angle of approximately \({\rm{111}}{\rm{.}}{{\rm{7}}^{\rm{^\circ }}}\)
Types of Ethers
Depending on the groups at \({\text{R}}\) and \({\text{R}}\)′, ethers are classified into two types:
1. Simple ethers or symmetrical ethers: These ethers consist of the same alkyl group at both ends of the oxygen atom. For example-
2. Mixed ethers or asymmetrical ethers: These ethers consist of different alkyl groups at both ends of the oxygen atom. For example-
Isomerism in Ether
Isomerism occurs when two or more chemical compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in their atoms’ structural arrangement. Compounds that exhibit the phenomenon of isomerism are known as isomers and differ in physical and chemical properties. Aliphatic Ethers can exhibit two different types of isomers.
These are-
1. Chain Isomerism
Ethers that bear the same molecular formula but different carbon chain skeletons on both sides of the oxygen atom are called chain isomers. For example- \({{\rm{C}}_4}{{\rm{H}}_{10}}{\rm{O}}\) exhibits two chain isomers. These are- Ethoxy ethane and Methoxy propane
\({\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{OC}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\) and \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{OC}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
2. Functional Isomerism
Compounds with the same molecular formula but differ in their functional groups exhibit functional isomerism. Ethers are isomeric with alcohol.
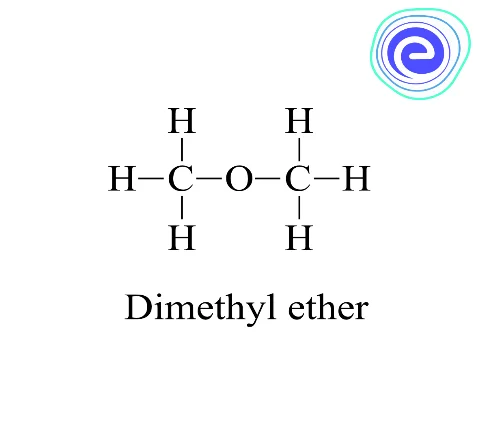
Example: dimethyl ether is isomeric with ethanol, and methyl ethyl ether is isomeric with propanol
3. Metamerism
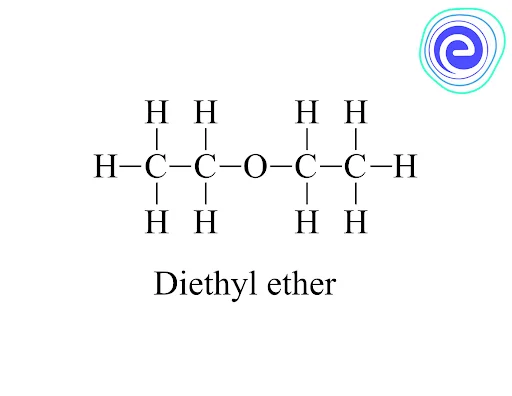
Metamers are isomers with the same chemical formula but distinct alkyl groups (around the functional group). Metamerism is shown by diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether. Both have an identical chemical formula; however, the alkyl groups on the sides are different.
Summary of Isomerism in Ethers
The structural formulas of ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether are different. Their molecular formula, however, is the same: \({{\rm{C}}_2}{{\rm{H}}_6}{\rm{O}}.\) These compounds not only have different structural formulas, but they also have different characteristics. As a result, a molecular formula can represent several compounds. Isomerism is the term for this phenomenon. Isomerism is made up of two words: iso and meros, which mean “same” and “parts.”
Ethers are the organic compounds in which an oxygen atom is present between the alkyl or aryl groups. The spatial arrangement of different atoms in ethers results in chain isomerism, functional isomerism and metamerism. In this article, we discussed the different isomerism of ethers along with their classification. We also learnt the difference between simple ethers and mixed ethers.
FAQs on Isomerism in Ethers
Q.1. What is the general formula of ethers?
Ans: It is represented by the general formula \({\rm{R – O – R}}\)’. The \({\text{R}}\)
,’ i.e. the hydrocarbon group in the formula, can be the same as \({\text{R}}\) or different.
Q.2. What is functional group isomerism in ethers?
Ans: An ether and monohydric alcohol containing the same numbers of carbon atoms are functional isomers. Example: \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3} – {\rm{O}} – {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\) dimethyl ether and \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{OH}}\) ethyl alcohol is the functional isomers.
Q.3. Which type of isomerism is shown by diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether?
Ans: Diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether molecules have the same number of atoms (four-carbon, one oxygen, and ten hydrogen atoms). They thus could be considered as ‘metamers’ in the old nomenclature. As the position of the oxygen atom and the branching of the carbon fragments varies, these molecules are now referred to as ‘constitutional isomers.’
Q.4. How are dimethyl ether and ethanol related?
Ans: Ethanol and dimethyl ether form a pair of functional isomers.
Q.5. What is the difference between chain isomerism and metamerism?
Ans: The main difference between position isomerism and metamerism is that, in position isomerism, the location of the functional group is changed whereas, in metamerism, the type of alkyl groups in the sides of the functional group is changed.