- Written By
Ankita Sahay
- Last Modified 31-12-2024
Precipitation: Introduction, Types, Examples, Various Factors
Precipitation: We all notice rainfall, snowfall, hailstorm, etc., coming from the clouds to the Earth’s surface. They all are forms of precipitation. The natural phenomenon by which any liquid or frozen water formed in the atmosphere, which falls back to the surface of the Earth is called precipitation. Rain, sleet, and snow all are forms of precipitation only. We all know very well the importance of the water cycle for sustaining life on Earth; along with the two natural phenomenons, evaporation and condensation, precipitation is one of the most important parts of the water cycle. In this article, we will gain knowledge regarding the meaning of precipitation, different forms of precipitation, how it occurs, classification of precipitation, and different examples of precipitation in detail.
From the chemistry point of view, precipitation is a chemical reaction in which two solutions of ionic substances are mixed to form an insoluble compound known as a precipitate. Similarly, in the atmosphere, water vapour gets saturated, and at a particular temperature, it gets condensed and precipitated.
Define Precipitation
Precipitation is defined as the process of the formation of a solid from a solution. In a liquid solution, when the reaction occurs, the solid substance that is formed is called a precipitate. The chemical which leads to the formation of the solid is called a precipitant. For example, precipitation occurs when any part of the atmosphere saturates itself with water vapour and with the required temperature, it condenses and precipitates. The cooling of the air molecules in the atmosphere and the incorporation of water vapour are the two processes that lead to precipitation in the atmosphere.
Learn About Transpiration Here
When the water vapour condenses into larger water droplets in the atmosphere, precipitation occurs. When these drops are heavy enough to be held in the clouds, they fall to the surface of the Earth in the form of rainfall. At higher altitudes, if precipitation occurs, the water droplets mayze into ice. These ice crystals then tend to fall to the Earth in the form of snow, hail, or rain, depending on the temperature within the clouds and at the surface of the Earth. Snow goes on melting as it comes near the surface of the Earth due to a rise in the temperature.
The smoke and dust particles present in the atmosphere act as condensation nuclei, and they form a surface to the water vapour to condense. This process goes on and gathers the droplets to form large droplets to fall on the Earth.
The different forms of precipitation are as follows:
1. Rain: Rain is the most common form of precipitation in which water droplets are of a size larger than (0.5{\rm{mm}}) and vary to (6{\rm{mm}}). Rainfall is the most vital form of precipitation, and therefore, the term precipitation mostly refers to rainfall. It is a great source of fresh water on the Earth.
2. Snow: The flaky form of ice crystals is known as snow and has an average density of \(0.1{\rm{g/cc}}\). This is also an important form of precipitation that usually forms in colder climates and higher altitudes.
3. Glaze orzing Rain: When rain or drizzles come in direct contact with the cold ground at about \({0^ \circ }{\rm{C}}\), the glaze is formed. In this process, the water dropsze to form an ice coating.
4. Drizzle: It appears as tiny water droplets floating in the air, and it is a fine sprinkle of very tiny water droplets of size less than 0.5mm and intensity greater than 1mm/h.
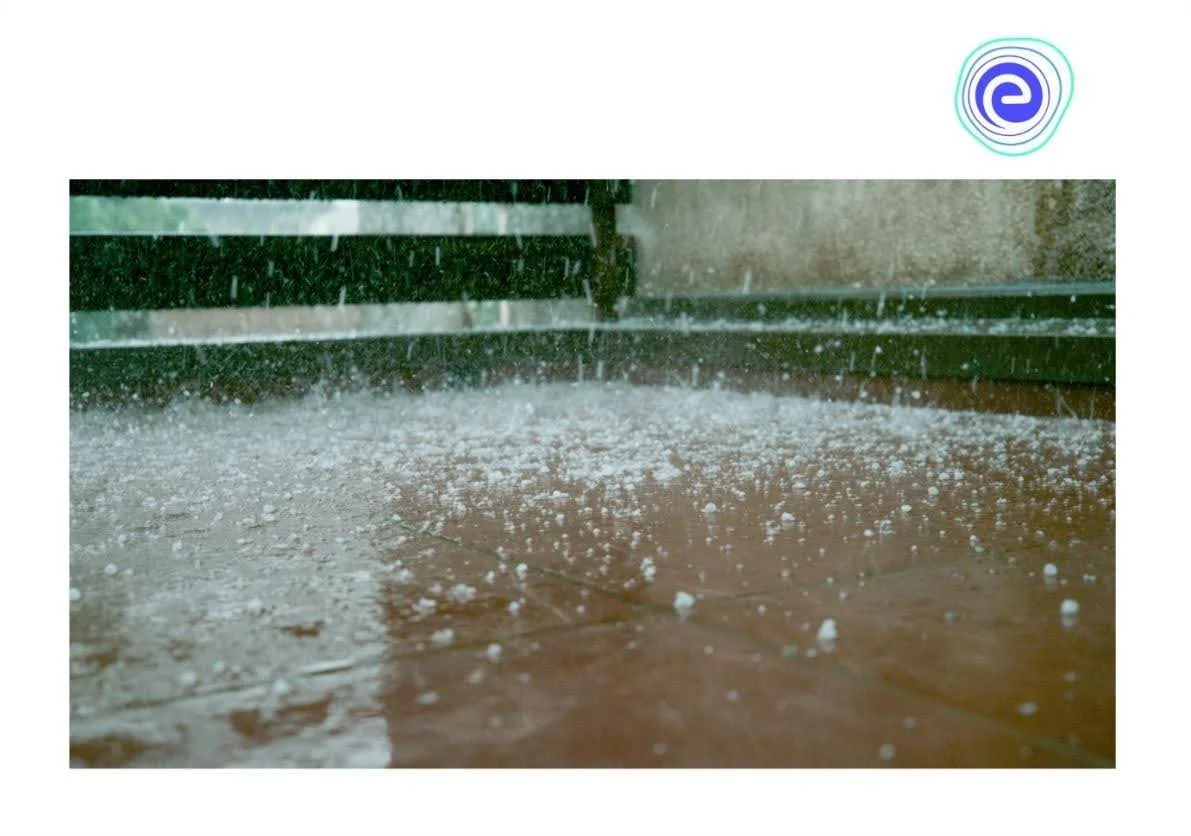
5. Hail: Hail is a kind of precipitation that showers in the form of pellets or lumps that look like ice and have a size greater than 8mm. Hail mostly occurs during thunderstorms.
6. Sleet: When rainfall passes through the air in the atmosphere at subfreezing or very low temperatures, frozen raindrops are formed, known as sleet.
Classification of Precipitation
When the mass of moist air undergoes the process of condensation, the process is known as precipitation. Thus, we can say that precipitation occurs when the air is cooled and saturated with the same amount of moisture, and this happens at higher altitudes. Therefore, based on the methods by which air mass can be lifted to higher altitudes, precipitation is classified into three different types, which are as follows:
- Cyclonic Precipitation
- Convective Precipitation
- Orographic Precipitation
1. Cyclonic Precipitation: A cyclone is a region in the atmosphere that has a very low pressure having circular wind motion. This cyclonic precipitation occurs by lifting of air mass and movement of moist air mass to this region caused due to pressure difference. Frontal and non-frontal precipitation are the two types of cyclonic precipitation.
a. Frontal Precipitation: The precipitation caused due to the expansion of air near the frontal surface is known as frontal precipitation. A frontal is known as the boundary of the hot moist air mass.
b. Non-Frontal Precipitation: The moist warm air mass is stationary, and the moving cold air mass meets it and form non-frontal precipitation.
2. Convective Precipitation
Mostly, the air above the land area gets heated, and most of this warmer air rises by the process of convection cools and gets precipitated. Convective precipitation is generally showery by nature and occurs in varying intensities.
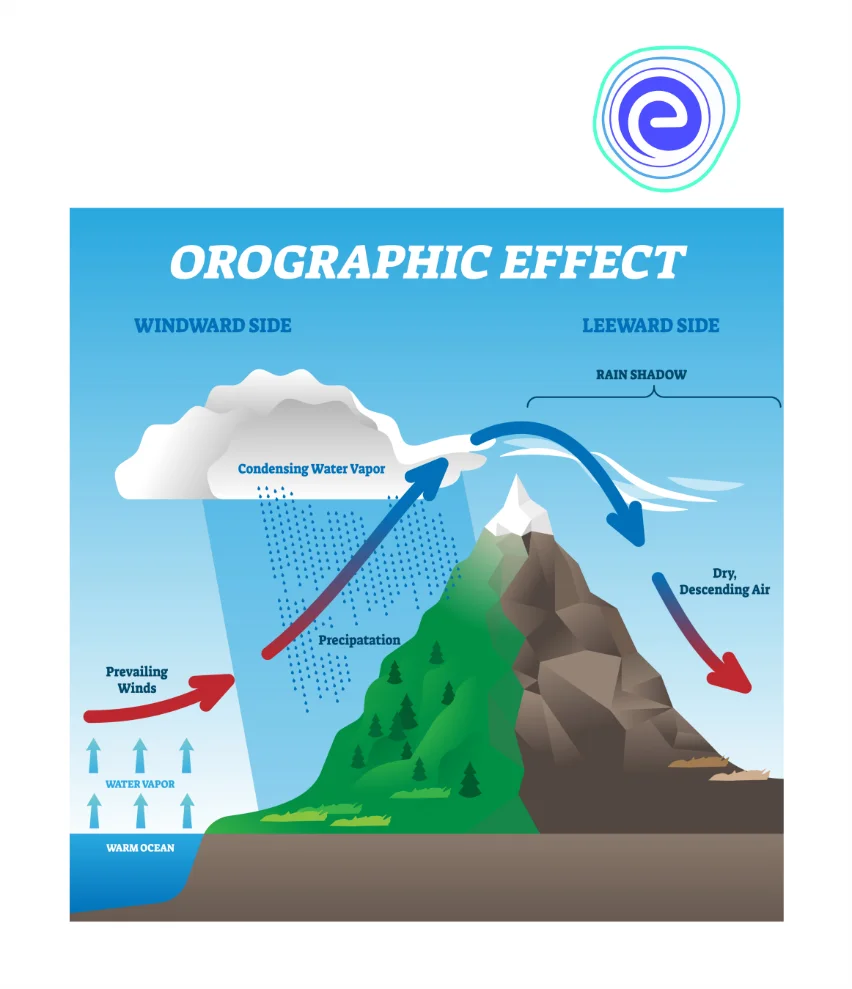
3. Orographic Precipitation
Sometimes, moving air masses strike barriers such as mountains or hills coming in its path. Once they strike, they rise and cause condensation and precipitation. More precipitation occurs in the windward side of the barrier compared to the leeward side of the barrier.
Factors Affecting Precipitation
- A lifting mechanism of air to cool the surrounding air.
- Condensation of water vapours and formation of cloud droplets in the atmosphere.
- Growth of the cloud droplets to such size that will be capable of falling to the ground against the lifting force of air.
- Presence of mountains and wind. A mountain range decides the place where the precipitation will fall.
- Temperature and humidity at a place are also deciding factors of precipitation.
In short, we can say that though we witness different types of rainfall, hailstorm, snowfall, etc., in different places, all are connected to each other, i.e., they all are different types of the same phenomena known as precipitation. Precipitation is defined as the process of the formation of a solid from a solution. In a liquid solution, when the reaction occurs, the solid substance that is formed is known as a precipitate. The two processes that lead to precipitation in the atmosphere are the cooling of air molecules in the atmosphere and the addition of water vapour to it.
Different examples or types of precipitation include rain, snowfall, hail, sleet, Gail, drizzle, etc. Based on the conditions and types of precipitation, it is classified into three types: cyclonic precipitation, convective precipitation, and orographic precipitation. There are various factors that affect the amount and type of precipitation in a particular area, such as the presence of the mountain range, the height of the mountain, direction of the wind, temperature, humidity, and many more. Thus, we can say that precipitation is an essential part of the water cycle on the Earth and plays a vital role in sustaining life on the Earth. Among all types of precipitation, rainfall is the leading feature of the climate.
FAQs on Precipitation
Q.1. What does precipitation mean? Ans: Precipitation means the process of the formation of a solid from a solution. In a liquid solution, when the reaction occurs, the solid substance that is formed is called a precipitate. The chemical which leads to the formation of the solid is called a precipitant. For example, precipitation occurs when any part of the atmosphere itself gets saturated with water vapour and with the required temperature, it gets condensed and precipitated. The cooling of the air molecules in the atmosphere and the incorporation of water vapour are the two processes that lead to precipitation in the atmosphere.
Q.2. What are three types of precipitation? Ans: The three types of precipitation include:
(i) Cyclonic Precipitation: A cyclone is a region in the atmosphere that has a very low pressure having circular wind motion. This cyclonic precipitation occurs by lifting of air mass and movement of moist air mass to this region caused due to pressure difference. Frontal and non-frontal precipitation are the two types of cyclonic precipitation.
(ii) Convective Precipitation: Mostly, the air above the land area gets heated, and most of this warmer air rises by the process of convection cools and gets precipitated. Convective precipitation is generally showery by nature and occurs in varying intensities.
(iii) Orographic Precipitation: Sometimes, moving air masses strike barriers such as mountains or hills coming in its path. Once they strike, they rise and cause condensation and precipitation. More precipitation occurs in the windward side of the barrier as compared to the leeward side of the barrier.
Q.3. What is precipitation, and examples? Ans: In the atmosphere, water vapour gets saturated, and at a particular temperature, it gets condensed and precipitated. This is called precipitation. Different examples of precipitation include rain, snowfall, hail, sleet, Gail, drizzle, etc.
Q.4. How do you identify a precipitate? Ans: A precipitate can be easily identified by its solubility. If the solute particles are not soluble in a solution and get precipitated or deposited at the bottom of the container, then the substance is known as a precipitate.
Q.5. Why is precipitation important to the water cycle? Ans: Precipitation is important to the water cycle because it is an essential part of the water cycle of the Earth and is necessary for maintaining the natural water balance. This helps in sustaining life and ecological balance on the Earth.
Learn Everything About Groundwater Here
We hope this article on Precipitation has helped you. If you have any queries, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you.