- Written By
Swati_C
- Last Modified 19-10-2024
The Breath of Life: Air – Composition, Pollution of Air
The Breath of Life – Air: Air is one of the most important life-supporting factors of the environment and can be termed “the breath of life”. Air is a mixture of various gases, water vapour and dust particles. It is colourless and odourless and is essential for living beings to survive on this earth.
So, what is air? How does air support our life? What are the ill effects of polluted air on our health? Why is air called the breath of life? In this article, we will help you understand all about Air – the Breath of Life. So, keep reading!
The Atmosphere and Its Importance
- The multi-layered gaseous envelope surrounding the planet Earth is called the atmosphere.
- The atmosphere extends to several kilometres in height from the surface of the Earth and is distinguished into four parts: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
- The troposphere is the lowest region of the atmosphere that contains air (oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen) and is subjected to differential heating.
- Living entities constitute the biotic component of the environment that interact with each other and their surrounding atmosphere.
A healthy atmosphere supports and influences life in the following ways:
- The ozone layer of the troposphere protects us from the harmful radiation of the Sun.
- The atmosphere helps to maintain the temperature on the Earth.
- It plays a very important role in the water cycle.
What is Air?
Air is a mixture of gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and other trace gases. Air also contains water vapour and suspended impurities (dust particles). When the air gets heated due to high temperature, it rises up and creates a low-pressure zone that attracts the cool air to move into its place from a high-pressure zone. The movement of air causes winds.
Learn Exam Concepts on Embibe
Composition of Air
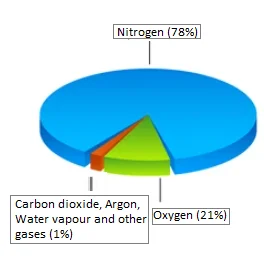
Air is a mixture of colourless and odourless gases. It is made up of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases (mainly including carbon dioxide and argon) and water vapour. The water vapour determines the moisture present in the air. The moisture content of the air varies from place to place. The arid region (the desert) has less moisture content compared to wetlands having plenty of rainfall.
Fig: Composition of Air
What is the Importance of Air?
In the sections below, we will talk about the environmental and biological importance of air.
Environmental Importance of Air
Air is an inexhaustible natural resource that is available in unlimited amounts. Just like water and other natural resources, the air is also important for the survival of living organisms. The main applications of air are as follows:
1. Air plays an important role in climate control. Air is a bad conductor of heat. Therefore, it helps to maintain the temperature of the Earth by circulating hot and cold air.
2. The circulation of air also contributes to the water cycle.
3. The moving air helps in the dispersal of seeds.
4. Air contains oxygen that helps in the burning (combustion) of fuels.
5. Nitrogen and carbon dioxide are required for plant growth and development.
6. Moving air facilitates the locomotion and migration of flying animals.
Biological Importance of Air in Humans
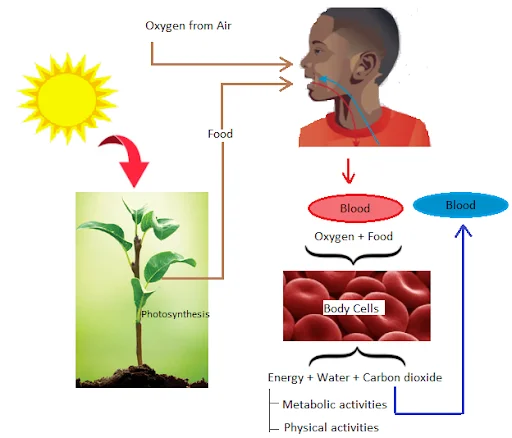
- Oxygen in the air is one of the major life-sustaining gases. Joseph Priestley discovered the oxygen. Living beings breathe in oxygen in order to obtain energy via the process of respiration. It can be said that “ Air is the breath of our life”.
- The oxygen is inhaled from the atmosphere during breathing.
- The oxygen gets diffused into the blood capillaries from the alveoli of the lungs and then reaches every cell of the body.
- Inside each cell, the oxygen combines with the food and breaks down food into carbon dioxide, water and energy are released. This process is called internal respiration.
- This energy remains stored in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) and is further utilised by the body cells to perform several physical and physiological activities.
- The carbon dioxide released is exhaled into the atmosphere and fixed by the plants in the process of photosynthesis.
- Nitrogen in a fixed form is required to build proteins and nucleic acids.
Practice Exam Questions
Fig: Importance of Air
Biological Importance of Air in Plants
- The stomata present on the surface of leaves, and lenticels on the stem absorb the oxygen from the air.
- The stems and roots are provided with an interconnected network of air spaces through which the oxygen diffuses from one cell to another.
- Nitrogen present in the air can be fixed by different microbes and then in turn those can be used by the plants.
- Nitrogen supports rapid growth in plants and encourages the healthy development of foliage and fruits.
- During the process of photosynthesis, the plants absorb carbon dioxide in order to produce glucose and oxygen.
Air Pollution and its Side-effects
The undesirable changes in the physical, chemical and biological properties of the environment are called pollution. Air pollution is defined as the contamination of air with foreign particles and gases that are harmful to humans, animals, vegetation, and buildings.
Causes
The major causes of air pollution include:
1. Burning of fossil fuels
2. Gas emitted by automobiles
3. Gas emitted by factories
4. Mining activities
5. Deforestation
Attempt Mock Tests
Side Effects of Air pollution on Human Health
- Polluted air causes shortness of breath, sore throat, and allergies to the respiratory tract.
- Fine particulate matter can cause cardiovascular diseases in severe conditions.
- Incomplete combustion of fuels releases carbon monoxide that is highly poisonous and reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the red blood cells.
- Air pollution can cause ozone layer depletion, which leads to the entry of harmful UV rays to enter our atmosphere.
- Air pollution also causes acid rain, global warming, etc.
Summary
The atmosphere is the part of the biosphere that is made up of different types of gases. The mixture of gases is called air. Air is an inexhaustible natural resource. We cannot imagine our life without air. Air which consists of oxygen is one of the main suppliers of energy. Cells are the basic structural unit of all living beings. These cells extract oxygen from the blood (in advanced animals) to produce energy in the form of ATP. The generation of ATP is essential to run several physical and metabolic activities and therefore maintains life on the Earth.
FAQs on The Breath of Life: Air
Q.1. Why is air called the breath of life?
Ans: Air is called the breath of life because it contains oxygen that is essential to sustain life. The carbon dioxide is utilised by the plant in the process of photosynthesis.
Q.2. What is the importance of air?
Ans: Air contains oxygen that combines with food and provides energy for various living activities. This process is called respiration. Plants utilise carbon dioxide for the synthesis of food required for plant growth and development.
Q.3. Who discovered oxygen?
Ans: Joseph Priestley discovered oxygen on 1st August 1774.
Q.4. How is carbon dioxide fixed in the atmosphere?
Ans: Carbon dioxide is fixed in the atmosphere by green plants during the process of photosynthesis.
Q.5. What do we exhale when we breathe?
Ans: All living beings (including plants, and animals) exhale carbon dioxide during breathing.
We hope this detailed article on The Breath of Life: Air helps you in your preparation. If you get stuck do let us know in the comments section below and we will get back to you at the earliest. Stay tuned to Embibe for more such information.