- Written By
Shalini Kaveripakam
- Last Modified 13-01-2025
Water a Precious Resource – Sources, Forms & Impact
Water is significantly necessary for life. There will be no life on Earth without water. Since water appears blue from space, our planet is called the “Blue Planet.” Do you know why the earth reflects blue light? It’s because water covers \(71\% \) of the earth’s surface, and water has a bluish reflection when viewed from a distance.
Oceans cover about \(70\% \) of the earth’s surface, whereas land accounts for only \(30\% \). Nearly \(1\% \) of the earth’s surface is covered by lakes and rivers. In the oceans, the water is saline. It’s useless for life on land. Freshwater is required for life on land. Rainfall is the principal source of fresh water on land. As a result, barely \(1\% \) of the world’s water is available for our domestic and agricultural requirements. In this article, let’s learn everything about water in detail.
Availability of Water in Nature
Water covers over \(71\% \) of the earth’s surface. Therefore, our earth is also called a watery planet.
Seas and oceans hold nearly \(97.5\) percent of the water available on the planet’s surface. This water is salty and inappropriate for human consumption because it cannot be consumed directly. A large amount \(\left({1.7\% }\right)\) of the remaining \(2.5\) percent is found frozen in the form of ice caps on the tops of mountains and glaciers.
River water accounts for only \(0.8\) percent of all freshwater. Lake and groundwater are also suitable for human consumption.
Water on the earth is available in three forms — solid, liquid and gas.
- Ice caps in the poles or other snow-covered mountains form the solid component.
- Rivers, lakes, and oceans constitute the liquid component.
- Water vapour in the atmosphere forms the gaseous component.
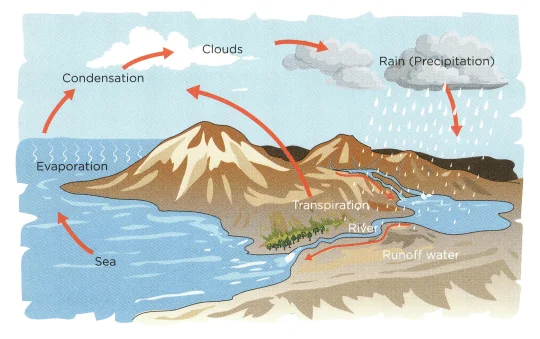
In nature, there exists a continuous circulation of water between the earth and the atmosphere. The cycle through which water is distributed in the biosphere is known as the water cycle or hydrological cycle. This cycle plays an important role in deciding the weather pattern for a place as well as the global climate.
Water Cycle
The water present on the earth’s surface evaporates continuously. The rate of evaporation of water is increased due to the heat of the Sun. The evaporated water when reaches the atmosphere; the cooler air condenses it into droplets. The droplets collectively form clouds. When clouds become heavy and cannot hold more water, the water droplets fall on the Earth as rain. This is called precipitation. After falling on the Earth, it again evaporates.
In a never-ending circle, this process repeats again and again. This cycle is called the water cycle or the hydrological cycle. The water cycle guarantees that all living organisms have access to water and regulates weather patterns on our planet.
Water: Sources
About three-fourths of the earth’s surface is covered with water. The various sources of water on the earth are rainwater and surface water, including river water, lake water, seawater and groundwater.
Rainwater
Rainwater is considered the purest form of naturally occurring water. However, gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide given out from the exhausts of vehicles, factories, etc., mix with air making rainwater acidic.
Surface Water
On the earth’s surface, water exists as snow, river water and seawater.
Snow
Water is found in the frozen state as snow.
River Water and Lake Water
The snow melts and changes into liquid water and flows into the lakes and rivers. Rainwater also fills the rivers, lakes, and ponds. Water in rivers, lakes, and ponds is not fit for drinking. It may contain germs and other soluble impurities. If consumed, it may cause waterborne diseases like typhoid, gastroenteritis, diarrhoea, etc.
Seawater
Have you ever tasted seawater? It is saline (salty). The river water flowing into the sea brings with its large quantities of salts which make it saline.
Groundwater
A lot of unseen water is hidden as groundwater. Groundwater is the water available under the ground. It is formed through rainwater when it seeps through various layers of porous rock and gets collected in the impervious layer of rock. The process through which it reaches this layer is known as infiltration. The top level of the groundwater is known as a water table. We use this water by digging wells or by using pumps to lift the water. When the groundwater is stored between two layers of hard rock, it is known as an aquifer.
Groundwater: Uses
- Groundwater has been utilized by digging wells deep till it reaches the water table.
- Manually operated hand-pumps or power-operated tube-wells are also used to pump out the groundwater.
- The groundwater is used for household (domestic), agricultural and industrial purposes. It provides moisture to the soil, which helps in the proper growth of plants.
Depletion of Water-Table
The gradual and continuous lowering of the water table is known as the depletion of the water table. It goes down if the groundwater is being used at a faster rate than it is being renewed by the natural processes.
Factors Responsible for the Depletion of Water Table
The following are the factors that affect the depletion of the water table
- Increase in Population: To meet the needs of an ever-increasing human population, more houses, offices, schools, shops, roads are being constructed, reducing the open space for seepage of rainwater into the ground. Secondly, boring is done to draw more and more groundwater.
- Increase in Industries: The number of industries is increasing continuously, which draws a huge quantity of water from the ground leading to the depletion of the water table.
- Increase in Agricultural Activities: With the increase in population, the demand for food has increased manifold. Most farmers depend on rainwater to grow crops, but due to unpredictable rainfall, they depend more on irrigation methods. Farmers use a large quantity of groundwater by digging deep tube wells to cultivate crops.
- Deforestation: Cutting down a large number of trees at a place is called deforestation. This is done to construct houses, offices, schools, roads, etc., thereby reducing the effective area for seepage of water.
- Scarcity of Rainfall: Some regions receive excessive rains, while some areas receive very little rainfall. Excessive rain causes floods, whereas the absence of rain results in droughts. When the rainfall is less than the average rainfall, it is called ‘scarcity rainfall’. When there is a scarcity of rainfall, more groundwater is drawn out to meet the required needs leading to depletion of the water table.
Water Management
Groundwater is available in abundance. But this does not mean that we should use it unmindfully. Different ways by which groundwater gets contaminated need to be properly looked into. This requires thoughtful management of water and cooperation on the part of the people and the government. Conservation of water is the best way to fulfil our demand for water. We can conserve water in many ways.
A water crisis is now a major threat to the existence of millions of people around the world. With changes in climatic conditions, increasing population and decline of rainfall in many areas, the time has come to get to the root cause of the problem and arrive at measures to control it. Water is a precious resource. To make water easily available for future generations, we have to conserve it today.
Some Steps to Conserve Water
- Repair a leaking tap immediately. Do not leave the water running from taps while washing, brushing and bathing.
- Dams and reservoirs should be constructed to collect water and control floods.
- Farmers should use better methods of irrigation like drip irrigation to use less water and still get good yields. They should also use natural fertilisers and pesticides to prevent contamination of groundwater.
- Water from industries should be recycled after proper treatment.
- More and more trees should be planted to prevent rainwater from flowing off and to allow water to seep into the ground to replenish the water table.
- Bawri is a step-well in which the rainwater is collected and stored. It provides water to the people during drought periods.
- Drip irrigation is a technique of watering plants by using a system of narrow pipes or tubes with small holes that deliver the water drop by drop directly around the roots. Thus, wastage of water is avoided.
Rainwater should be harvested and saved using the right techniques. Rainwater harvesting collects rainwater falling on roofs of buildings in a trench below the ground in huge buildings and small tanks in houses and small buildings. This collected rainwater can be put to many uses, such as washing cars, watering plants and so on.
Effect of Water Scarcity on Plants
Just like humans, plants need water for their survival. If we fail to save water in the coming days, no water will be available for the plants. It may cause the death of plants. As a result, we will have no food to eat, no oxygen to breathe, and no rain to recharge the groundwater. Therefore, act now and do your part in saving water.
The Best Way of Overcoming Water Shortage: Rainwater Harvesting
We will now describe two cases in which the people have successfully overcome the acute water shortage in their area by practising rainwater harvesting.
Case 1. A place called Bhojpuri in the Kutch area of Gujarat State has a very erratic rainfall (very irregular rainfall). The only source of fresh water in this area is groundwater because the rivers in this area do not have water throughout the year. With the increase in population, the demand for water has grown too much over the years.
Due to this, the drawing of groundwater (through wells and tube-wells, etc.) has far exceeded the natural recharge by the seepage of rainwater. As a result, the water table in this area went down, and some of the wells and tube wells dried up completely.
In \(1989\), the village people, and a Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO), decided to harvest rainwater. For this purpose, \(18\) check-dams were built on the Rukmavati river and its many tributaries flowing through the area. The rainwater held by check-dams seeped into the ground and recharged the groundwater in aquifers. As a result of this, all the wells and tube-wells in this area have sufficient water now. As a result, river water (essentially rainwater) that was previously wasted by flowing into the sea has become available as groundwater for irrigation and other uses.
Case 2. Rajasthan is a hot and dry region with little rainfall. The problem of natural water scarcity has been successfully overcome due to people’s collective action. Five dried-up rivers, Arveri, Ruparel, Sarsa, Bhagani, and Jahazwali, have been resurrected by a group of social workers who built rainwater harvesting facilities. The increased water thus available has transformed a dry area in the Alwar District of Rajasthan into a lush green area.
Summary of Water a Precious Resource
One of the most prevalent and useful things in our environment is water. Water is required for the survival of all living things. Water is required for the survival of all living things (humans, other animals, and plants). There would be no living beings on the planet if it didn’t have water.
On this planet, there is an abundance of water. The seas and oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, snow-covered mountains, glaciers, polar ice caps, groundwater, and the atmosphere hold nearly all of the water on the planet. We learned about the water cycle, water sources, depletion of the water table, the impact of water on plant shortages, and rainwater collection in this post.
Frequently Asked Questions on Water
Frequently asked questions related to water are listed as follows:
Q. Is water the most precious resource?
Ans: Yes, our most valuable resource is water. We drink about four litres of water every day on average, and it is an essential component of our industry and agriculture. It is, after all, at the very core of our existence. The importance of water management has dominated human history.
Q. What are the sources of water?
Ans: The various sources of water on the earth are rainwater and surface water, including river water, lake water, seawater and groundwater.
Q. How do you think water is a precious resource?
Ans: Water is an inexhaustible resource. It is required by all living things and must be carefully controlled to ensure that we have enough to meet our needs even while protecting the environment. Water is a valuable resource.
Q. How is water precious in our life?
Ans: Water is a valuable resource. Let’s try to save it. Water is necessary for every life on the planet. Water is essential for both plants and animals to survive. Water is necessary for food security, animal security, organic life, industrial production, biodiversity and environmental conservation.
Q. What is water important for us?
Ans: Water is used by your body to regulate temperature and maintain other bodily functions in all of its cells, organs, and tissues. Because your body loses water through breathing, sweating, and digesting, it’s critical to rehydrate by drinking water and consuming water-rich foods.
Q. What are the uses of water?
Ans: There are three uses if water, which are, domestic use, industrial use and uses of water as a habitat.
We hope this article on ‘Water: A Precious Resource’ has helped you. If you have any queries, drop a comment below, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.