39 Insightful Publications
The experiment “Image of an Object Beyond 2F by a Convex Lens” aims to study the refraction of light through a lens. The objective of this experiment is to observe the image formed for an object placed beyond the centre of curvature of a convex lens.
How Are Images Formed by a Convex Lens?
A convex lens bulges outward and is thicker in the middle and thinner at the upper and lower edges. A convex lens forms images through the refraction of light passing through it. When refracted through a convex lens, the light rays obey the laws of refraction. A convex lens converges the light rays parallel to the principal axis towards the focal point, as shown in the figure below:
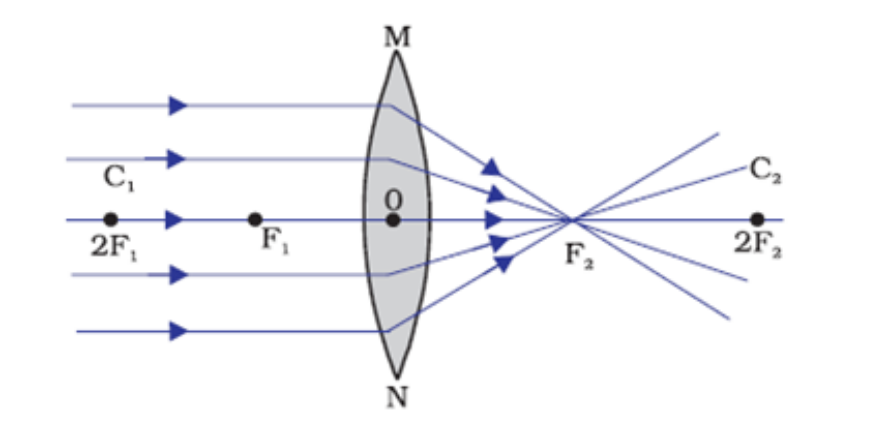
Hence, convex lenses are called converging lenses.
Light rays passing through the edges of a convex lens are bent most, whereas light passing through the lens’s centre remains straight.
A convex lens forms either a real or virtual image. It depends on how close the object is to the lens relative to the focus.
- Case 1: A real, inverted image will be formed for an object outside the focal point.
- Case 2: For an object inside the focal point, a virtual erect image will be formed.
Convex lenses are the only lenses that can form real images. Unlike a virtual image, a real image appears where the light converges.
Diagram – Image of an Object Placed Beyond 2F of a Convex Lens
When the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature (2F) of a convex lens, a real, inverted and diminished image is obtained via the convex lens, as shown in the figure below.

What Are The Rules for Image Formed by a Convex Lens?
For drawing ray diagrams, only two rays are considered for clarity. The intersection of at least two refracted rays gives the position of the image of the point object. Any two of the following rays can be considered for locating the image:
- Rule 1: An incident ray travelling parallel to the principal axis after refraction through the convex lens passes through the focal point on the other side.
- Rule 2: An incident ray passing through the first principal focus of a convex lens emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
- Rule 3: A ray of light, passing through the optical centre of the lens, emerges without any deviation after refraction.
FAQs on Image of an Object Beyond 2F by a Convex Lens
1. What is the position of the image formed when the object is placed beyond 2F in front of a convex lens?
Ans: Between F and 2F.
2. Is the magnitude of magnification of the image formed in the above case greater than or less than 1?
Ans: The image formed is smaller than the size of the object. Hence, the magnitude of magnification is less than 1.
3. Can the above image be obtained on a screen?
Ans: Yes, since the actual intersection of rays forms the image, it can be obtained on a screen.
4. According to the optical coordinate system, the height of the image above the principal axis is taken as positive or negative.
Ans: Positive.
5. For a medium with a higher refractive index, the speed of light in that medium will be _______.
Ans: Slower.




























