39 Insightful Publications
The experiment “Convert Given Galvanometer Into a Voltmeter” aims to convert a given galvanometer of known resistance and figure of merit into a voltmeter of the desired range and to verify the same.
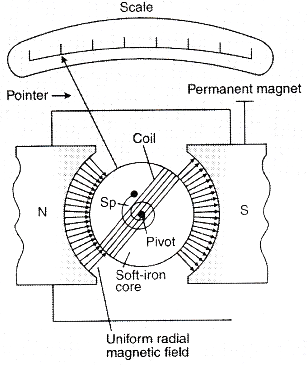
What is a Galvanometer?
An electromechanical instrument that is used for noticing & signifying an electric current is known as a galvanometer. Simply put, we can say that it is used to detect small electric currents or measure their magnitude. The current and its intensity are usually indicated by a magnetic needle’s movement or that of a coil in a magnetic field, which is an important part of a galvanometer.
The main function of the galvanometer is to decide the current’s existence, direction, and strength in an element/circuit. This works on the rule of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
What is a Voltmeter?
The instrument which measures the voltage or potential difference in volts is known as the voltmeter. It works on the principle that the torque is generated by the current which induces because of measured voltage, and this torque deflects the pointer of the instrument. The deflection of the pointer is directly proportional to the potential difference between the points. The voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the circuit/element across which the potential difference has to be measured.

How Can You Transform a Galvanometer to Voltmeter?
A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a high-resistance in-series connection. The scale is calibrated in volt. The value of the resistance connected in series decides the range of the voltmeter.

Galvanometer resistance = G
The current required to produce full-scale Deflection in the galvanometer =Ig
Range of voltmeters =V
Resistance of voltmeter =R
Since R is connected in series with the galvanometer, the current through the galvanometer,
Ig=R+GV
∴ R=V/Ig −G
The resistance is calculated by this equation, which is connected in series. The effective resistance of the voltmeter is Rv=G+R. Rv is very large, and hence, a voltmeter is connected in parallel in a circuit as it draws the least current from the circuit.
FAQs on Transforming Galvanometer to Voltmeter
What is the principle of working on a galvanometer?
Ans: A galvanometer works on the principle of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
What is a voltmeter?
Ans: It is a device that measures the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit.
How is a galvanometer converted into a voltmeter?
Ans: A galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance in series with the galvanometer.
Can we measure heavy currents using a galvanometer?
Ans: No
What do you understand by the term ‘ideal voltmeter’?
Ans: An ideal voltmeter is a voltmeter which does not draw any current from the circuit to which it is connected, in other words, we can say that it has infinite resistance.




























