39 Insightful Publications
Fluids: Fluids are substances that can flow and take the shape of their container. Liquids and gasses are both considered fluids.
Density: Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume. It’s typically denoted by the symbol “ρ” (rho). The formula for density is: Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V). The SI unit for density is kg/m³.
Buoyancy: Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it. It counteracts the force of gravity.
Archimedes’ Principle:
When a body is partially or fully immersed in a fluid at rest, the fluid exerts an upward force of buoyancy equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the body.
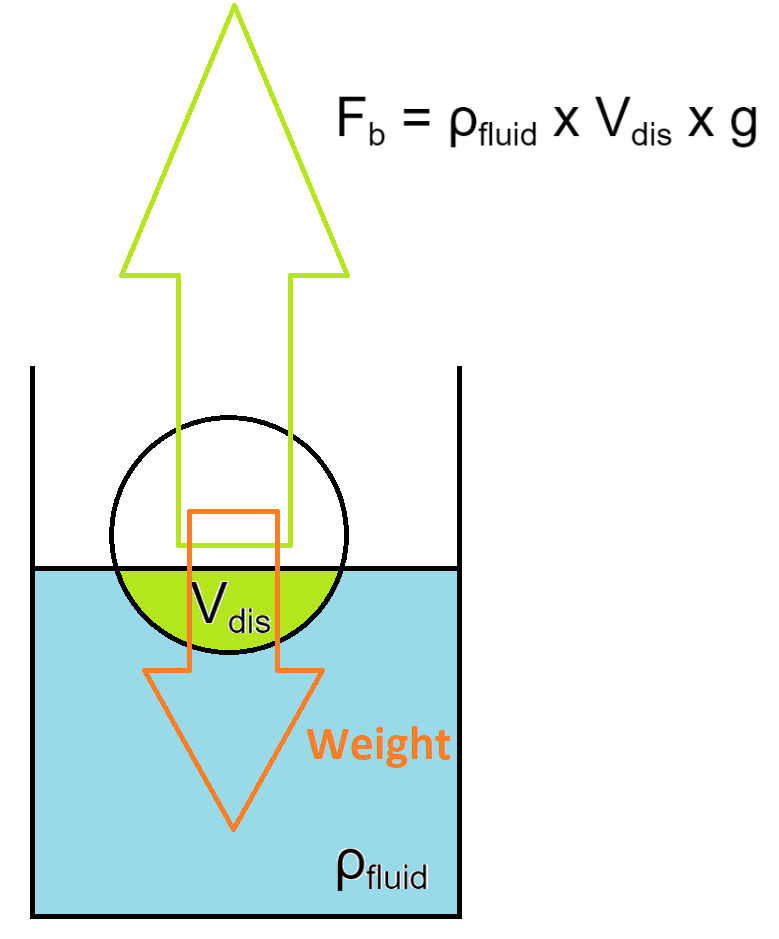
Buoyant Force: The buoyant force (Fb) can be calculated using the formula:
Fb = ρfluid x Vdis x g
Where
ρfluid is the density of the fluid,
Vdis is the volume of fluid displaced by the submerged part of the object, and
g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Floatation:
If ρsolid < ρfluid The object floats in the fluid with only a fraction of it in the fluid.
If ρsolid = ρfluid The object floats in the fluid completely immersed wherever it is left in the fluid.
If ρsolid > ρfluid The object sinks in the fluid.

FAQs on Archimedes’ Principle
What does Archimedes’ Principle state?
Answer: An object in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid.
How does fluid density relate to Archimedes’ Principle?
Answer: Density affects buoyancy force, with less dense objects experiencing greater buoyancy.
Why does an object float or sink?
Answer: If its density is less than the fluid, it floats; if it is greater, it sinks.
Why do bubbles in a drink rise?
Answer: Buoyant force is greater than the weight of the bubble.
Why does an ice cube float in a glass of water, even though ice is solid?
Answer: Because the density of ice is less than that of water.




























