A Team of Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
A Team of Subject Experts Biology Solutions for Exercise - A Team of Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Unit I: Diversity in the Living World Unit II: Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from A Team of Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
What is correct for monocotyledons?
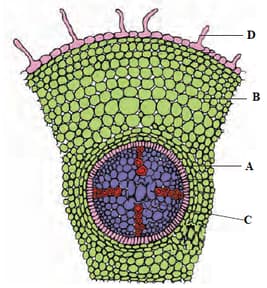
Select the incorrect option with respect to the given anatomy of the plant part.

The dorsiventral leaf of the plant has
(a) Conspicuous cuticle present on both epidermis.
(b) Palisade tissue towards the abaxial epidermis and spongy parenchyma towards the adaxial epidermis.
(c) Bulliform cells in the adaxial epidermis.
(d) Vascular bundles surrounded by a layer of thick-walled bundle sheath cells.
Mark A, B, C, and D in the given figure.
Leaves of monocotyledonous plants generally do not possess
Select the incorrect statements from the given below.
(i) The parallel venation in monocot leaves is reflected in the near sizes of vascular bundles except in the main vein.
(ii) Starch sheath is present in root endodermis with Casparian strips on tangential and radial walls.
(iii) Conjunctive tissue is parenchymatous cells, which lie between the xylem and phloem in the dicot root.
(iv) In maize stem, vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissue with smaller towards the center and larger towards the periphery.
A transverse section of a typical monocot root shows
(a) Barrel-shaped endodermal cells with casparian strips.
(b) Diarch to hexarch vascular bundles.
(c) Protoxylem towards center
and metaxylem towards periphery.
(d) Large well-developed parenchymatous pith in center.
Leaves of grasses roll and unroll due to
