Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise-2
Simple step-by-step solutions to Exercise-2 questions of Work, Energy and Power from Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
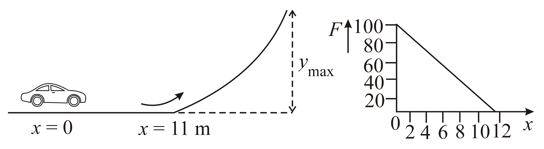
A toy car of mass starts from rest and moves up a ramp under the influence of force ( is applied in the direction of velocity) plotted against displacement The maximum height attained is given by
A spring of spring constant placed horizontally on a rough horizontal surface is compressed against a block of mass placed on the surface so as to store maximum energy in the spring. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is the potential energy stored the spring is:
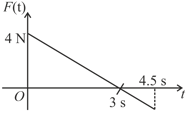
A block of mass is free to move along the -axis. It is at rest and from onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force in the direction. The force varies with as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after seconds is:
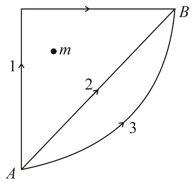
If and represent the work done in moving a particle from to along three different paths respectively (as shown) in the gravitational field of a point mass find the correct relation between and
Assertion : The instantaneous power of an agent is measured as the dot product of instantaneous velocity and the force (only one force applied by agent) acting on it at that instant.
Reason : The unit of instantaneous power is watt.
Assertion : When the force retards the motion of a body, the work done is zero.
Reason : Work done depends on angle between force and displacement.
Assertion: In a perfectly inelastic collision between two spheres, velocity of both spheres just after the collision are not always equal.
Reason: For two spheres undergoing collision, component of velocities of both spheres along line of impact just after the collision will be equal if the collision is perfectly inelastic. The component of velocity of each sphere perpendicular to line of impact remains unchanged due to the impact.
When a work is done on a body by an external force then, its
