Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: Does Organic Chemistry Mean We Can Make Any Substance We Want?, Exercise 21: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Annie Termaat Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: Does Organic Chemistry Mean We Can Make Any Substance We Want?, Exercise 21: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 12: Does Organic Chemistry Mean We Can Make Any Substance We Want?, Exercise 21: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MYP By Concept 4&5 Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: Does Organic Chemistry Mean We Can Make Any Substance We Want?, Exercise 21: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with Hints & Solutions
Outline an experimental approach that could demonstrate the complete combustion of hydrocarbons results in the formation of carbon dioxide and water.
Explain why methanol, ethanol, propan--ol and butan--ol are all highly soluble in water, but pentan--ol is far less soluble and decan--ol is almost insoluble at .
Methanol, ethanol, propan--ol and butan--ol are all highly soluble in water, but pentan--ol is far less soluble and decan--ol is almost insoluble at .
A fresh ball of cotton wool is dipped into each of the alcohols listed above and rubbed across a piece of dark paper to produce a series of six ‘wet marks’. Predict, with reasons, the order in which the marks will evaporate to dryness.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
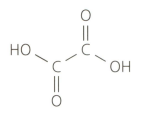
Suggest why ethanedioic acid is described as a dibasic acid in an aqueous solution.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
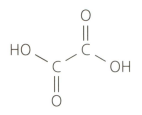
Deduce the molecular and empirical formulas of ethanedioic acid.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
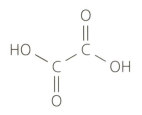
Formulate an equation showing the neutralization of ethanedioic acid by barium hydroxide solution.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
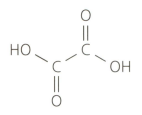
Suggest why aluminium saucepans become shiny and clean after stewing with rhubarb leaves.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
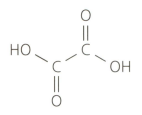
Suggest a name for the salt formed between ethanedioic acid and potassium carbonate. Formulate the equation for the reaction.
