Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What are the Impacts of Chemical Industry?, Exercise 20: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Annie Termaat Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What are the Impacts of Chemical Industry?, Exercise 20: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: What are the Impacts of Chemical Industry?, Exercise 20: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MYP By Concept 4&5 Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What are the Impacts of Chemical Industry?, Exercise 20: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with Hints & Solutions
Table lists the strength of various acids, familiar and unfamiliar, and their dissociation in water. Analyse the information and make a scientifically supported judgement about acid that have more than one ionisable hydrogen atom in their molecule or ions.
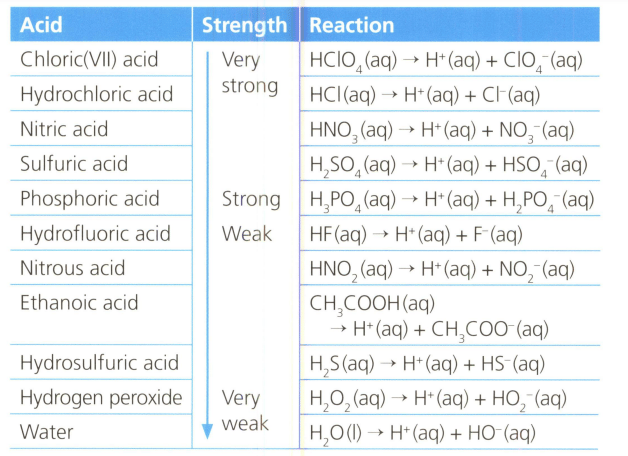
Use the Bronsted-Lowry theory to explain (with examples) why water is amphoteric in acid-base reaction.
Explain the distinction between strong and weak versus concentrated and dilute acids. Include diagrams to represent these concepts.
The definitions below represent some of the emerging ideas by scientists reflecting on the chemistry of acids and bases.

Analyse and evaluate these definitions and make scientifically supported judgement about whether any parts of these definitions are satisfactory in the light of your knowledge.
The is a constant for the extent that pure water molecules dissociates into its component ions, protons and hydroxide ions . The value is the product of the hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion concentrations (or alternatively the square of the hydrogen ion concentration).
Table compares the extent that pure water molecules dissociates at different temperatures, and very precise measurements of pH values.
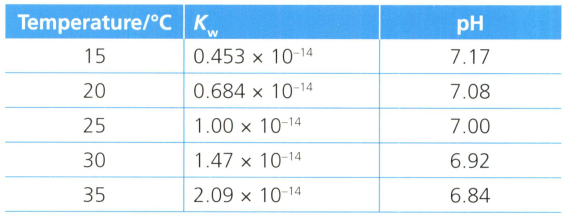
Describe the trends in the extent that water molecules in sample of water dissociate with an increase in temperature.
The is a constant for the extent that pure water molecules dissociates into its component ions, protons and hydroxide ions . The value is the product of the hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion concentrations (or alternatively the square of the hydrogen ion concentration).
Table compares the extent that pure water molecules dissociates at different temperatures, and very precise measurements of pH values.
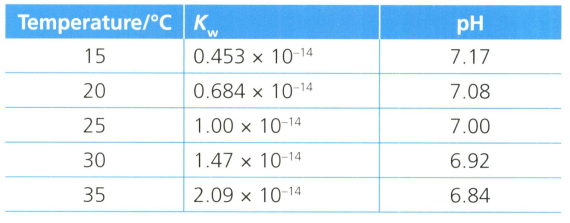
Explain why the pH changes in response to the dissociation of water molecules. What does pH measure?
Use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory to write an equation showing how to water molecules react together and produce ions.
As the number of ions present in the pure water changes with temperature, can we water still be considered neutral? Explain your reasoning.
