Arun Sharma Solutions for Exercise 2: Level of Difficulty
Arun Sharma Quantitative Aptitude Solutions for Exercise - Arun Sharma Solutions for Exercise 2: Level of Difficulty
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 2: Level of Difficulty with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. How to prepare for Quantitative Aptitude for the CAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Arun Sharma Solutions for Exercise 2: Level of Difficulty with Hints & Solutions
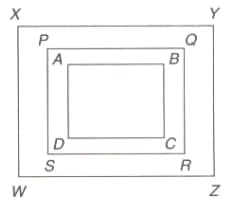
In a are points on sides such that . What is the ratio of the area of quadrialteral to that of ?
is a square with sides of length units. is an isosceles triangle with base . cuts at point and cuts at point . The area of trapezoid is square units. The altitude from of the triangle is:
In a triangle the length of side is . If the length of side is a perfect square, then the length of side is a power of and the length of side is twice the length of side . Determine the perimeter of the triangle.
is a parallelogram with . If the longer diagonal is of length and the area of the parallelogram is , then the perimeter of the parallelogram (in ) is:
A city has a park shaped as a right angled triangle. The length of the longest side of this park is . The Mayor of the city wants to construct three paths from the corner point opposite to the longest side such that these three paths divide the longest side into four equal segments. Determine the sum of the squares of the lengths of the three paths (in )
Let be the circle of radius . square is inscribed in such that all the vertices of the square lie on the circumference of . Another square is inscribed in the circle . Circle is inscribed in the square and so on. If is the area between and where represents the set of natural numbers. If the ratio of sum of all such to that of the area of the square is then ?
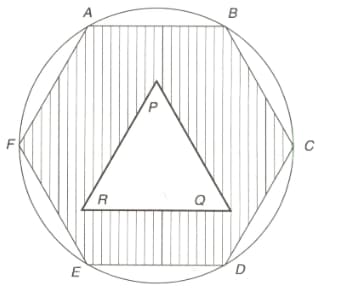
In the figure, is a regular hexagon and is an equilateral triangle of side ''. The area of the shaded portion is and .
If the area of the circle circumscribing the hexagon is then
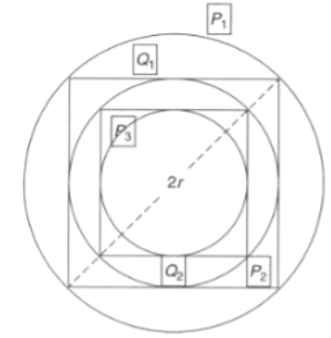
A series of infinite concentric squares are drawn as shown below. Starting with the first square subsequent squares drawn are and so on as shown in the diagram. If areas of the squares are and so on, then find the area of the diagram when the infinite number square is drawn.