B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Capacitor and Capacitance, Exercise 1: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Capacitor and Capacitance, Exercise 1: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Capacitor and Capacitance, Exercise 1: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Electrostatics and Current Electricity JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Capacitor and Capacitance, Exercise 1: DPP with Hints & Solutions
A capacitor is charged by using a battery, which is then disconnected. A dielectric slab is then slipped between the plates, which results in
The capacity and the energy stored in a parallel plate condenser with air between its plates are respectively and If the air is replaced by glass (dielectric constant ) between the plates, the capacity of the plates and the energy stored in it will, respectively, be
A parallel plate capacitor having a plate separation of is charged by connecting it to a supply. The energy density is
A parallel plate capacitor (without dielectric) is charged by a battery and kept connected to the battery. A dielectric slab of dielectric constant is inserted between the plates, fully occupying the space between the plates. The energy density of electric field between the plates will
An uncharged parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery. The electric field between the plates is . Now, a dielectric of dielectric constant is inserted between the plates, filling the entire space. The electric field between the plates now is
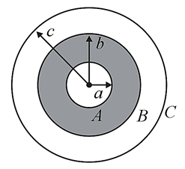
and are concentric conducting spherical shells of radius and , respectively. is surrounded by a concentric-dielectric medium of inner radius outer radius and dielectric constant If the sphere is given a charge the potential at the outer surface of the dielectric is
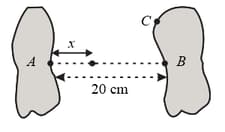
Two metallic bodies separated by a distance are given equal and opposite charges of magnitude . The component of the electric field along the line , between the plates, varies as to , where (in meters) is the distance from one body towards the other body as shown.
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor with no dielectric are connected to a voltage source. Now, a dielectric of dielectric constant is inserted to fill the whole space between the plates with voltage source remaining connected to the capacitor. What will happen?
