B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 1: Concept Application Exercise
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 1: Concept Application Exercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 1: Concept Application Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS for Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Electrostatics and Current Electricity solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 1: Concept Application Exercise with Hints & Solutions
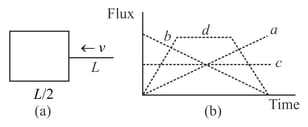
Figure (a) shows an imaginary cube of edge . A uniformly charged rod of length moves towards left at a small but constant speed At the left end of the rod just touches the right face of the cube. Which of the graphs in the Figure (b) represents the flux of the electric field through the cube as the rod goes through it?
A uniform electric field intersects a surface of area . What is the flux through this area if the surface lies (a) in the plane, (b) in the plane, (c) in the plane?
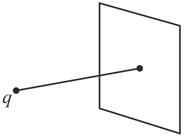
(a) A point charge is located at distance from an infinite plane. Determine the electric flux through the plane due to the point charge.
(b) A point charge is located at a very small distance from the center of a very large square on the line perpendicular to the square passing through its center. Determine the approximate electric flux through the square due to the point charge.
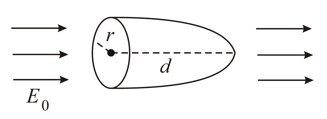
Calculate the total electric flux through the paraboloidal surface due to a uniform electric field of magnitude in the direction shown in figure.
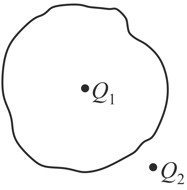
Consider a closed surface of arbitrary shape as shown in figure. Suppose a single charge , is located at some point, within the surface and the second charge is located outside the surface.
(a) What is the total flux passing through the surface due to charge ?
(b) What is the total flux passing through the surface due to charge ?
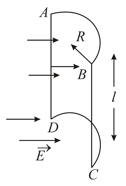
A hollow half-cylinder surface of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field . Electric field is acting perpendicular on the plane . Find the flux through the curved surface of the hollow cylindrical surface.
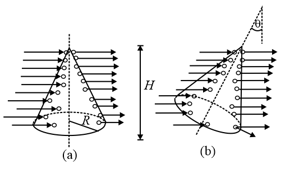
A cone of radius and height is placed in an uniform electric field as shown in the figure (a), if the axis of the cone made inclined with the vertical as shown in the figure (b). Calculate the flux of electric field entering the cone.
Point charge is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. The flux of Electric field through the square caused due to charge is . If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density , find the magnitude of the force on the square surface due to point charge .