B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: Concept Application Exercise
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: Concept Application Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: Concept Application Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS for Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Electrostatics and Current Electricity solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: Concept Application Exercise with Hints & Solutions
A conducting sphere carrying charge is surrounded by a spherical conducting shell.
(a) What is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(b) Another charge is placed outside the shell. Now, what is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(c) If is moved to a position between the shell and the sphere, what is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(d) Are your answers valid if the sphere and shell are not concentric?
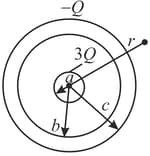
A solid insulating sphere of radius carries a net positive charge , uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with an inner radius and outer radius and having a net charge , as shown in the figure.
(a) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(b) The direction of the electric field is ___ .
(c) The electric field at is _____.
(d) The electric field in the region with radius , where , is _____.
(e) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , where , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(f) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , where , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(g) The electric field in the region is _____.
(h) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius . Find an expression for the net charge enclosed by this surface as a function of . Note that the charge inside this surface is less than .
(i) The electric field in the region is _____.
(j) The charge on the inner surface of the conducting shell is _____.
(k) The charge on the outer surface of the conducting shell is _____.
(l) Make a plot of the magnitude of the electric field versus .
Which of the following statements is correct? If , at all points of a closed surface,
(a) the electric flux through the surface is zero.
(b) the total charge enclosed by the surface is zero.
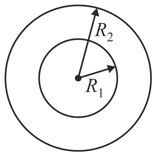
A hollow dielectric sphere, as shown in figure, has inner and outer radii of and , respectively. The total charge carried by the sphere is , this charge is uniformly distributed and
(a) Then, the electric field for is zero. (Yes/No)
(b) Then, the electric field for is given by ______.
(c) Then, the electric field for is given by _____.
A ring of diameter is rotated in a uniform electric field until the position of maximum electric flux is found. The flux is found to be . What is the electric field strength?
Consider two concentric conducting spheres. The outer sphere is hollow and initially has a charge on it. The inner sphere is solid and has a charge on it.
(a) How much charge is on the outer surface and inner surface of the outer sphere.
(b) If a wire is connected between the inner and outer sphere, after electrostatic equilibrium is established how much total charge is on the outer sphere? How much charge is on the outer surface and inner surface of the outer sphere? Does the electric field at the surface of the inside sphere change· when the wire is connected?
(c) We return to original condition in (a). We now connect the outer sphere to ground with a wire and then disconnect it. How much total charge will be on the outer sphere? How much charge will be on the inner surface and outer surface of the outer sphere?
In an insulating medium (dielectric constant ) the charge density varies with -coordinate as , where is a positive constant. The electric field is zero at and everywhere else it is along -direction. Calculate the electric field as a function of .
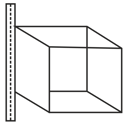
An infinite wire having charge density passes through one of the edges of a cube having edge length . Find the
(a) total flux passing through the cube,
(b) flux passing through the surfaces which are in contact with the wire,
(c) flux passing through the surfaces which are not in contact with the wire.