B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rigid Body Dynamics: Part 1, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rigid Body Dynamics: Part 1, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 3: Rigid Body Dynamics: Part 1, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rigid Body Dynamics: Part 1, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with Hints & Solutions
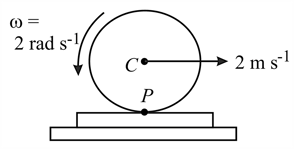
A disc of radius is rolling on a plank. If the disc is moving on the plank with angular velocity and speed Find the speed of the plank for pure rolling.
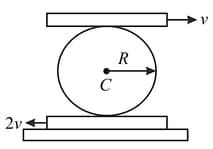
A uniform disc of radius rolls perfectly over two horizontal plank and moving with velocities and respectively. Find the
(a) velocity of of the disc.
(b) angular velocity of the disc
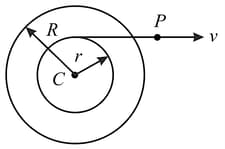
A cotton reel rolls without sliding such that the point of the string has velocity Find the:
(i) velocity of its centre
(ii) angular velocity of the cotton reel.
Two wheels and of radii and are connected by a belt. If the belt does not slide over the wheels, find the:
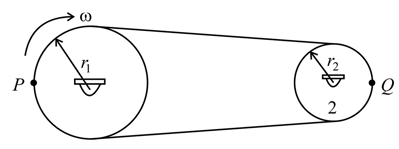
(i) speed of a point on the belt.
(ii) angular velocity of the wheel
(iii) acceleration of relative to
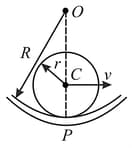
A cylinder of radius rolls perfectly with a speed on a concave surface of radius Find the acceleration of the bottom of the rolling body.
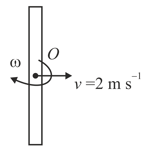
Shown in the figure is a rod which moves with and rotates with Find the instantaneous axis of rotation.
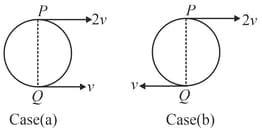
Find the position of instantaneous centre of rotation and angular velocity of the disc in the following cases as shown. Radius of disc is in each case.
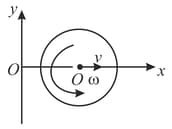
A rotating disc moves in the positive direction of -axis as shown. Find the equation describing the position of the instantaneous axis of rotation if at the initial moment the centre of the disc was located at origin after which
(a) it moved with constant acceleration (initial velocity zero) while the disc rotating anticlockwise with constant angular velocity
(b) it moved with constant velocity while the disc started rotating anticlockwise with a constant angular acceleration (with initial angular velocity zero).