BM Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion I, Exercise 7: DPP
BM Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - BM Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion I, Exercise 7: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 6: Newton's Laws of Motion I, Exercise 7: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Mechanics I JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from BM Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion I, Exercise 7: DPP with Hints & Solutions
A spring balance and a physical balance are kept in a lift. In these balances, equal masses are placed. Now, if the lift starts moving upwards with constant acceleration, then,
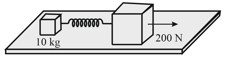
The masses of and , respectively, are connected by a massless spring, as shown in the figure. A force of acts on the mass. At the instant shown, the mass has acceleration . What is the acceleration of mass?
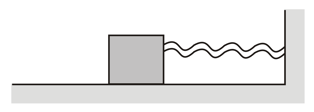
An ideal spring is compressed and placed horizontally between a vertical fixed wall and a block, free to slide over a smooth horizontal tabletop as shown in the figure. The system is released from rest. The graph which represents the relation between the magnitude of the acceleration of the block and the distance travelled by it (as long as the spring is compressed) is,
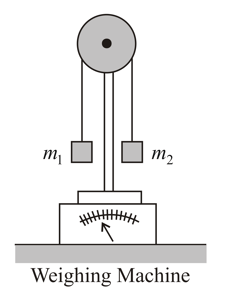
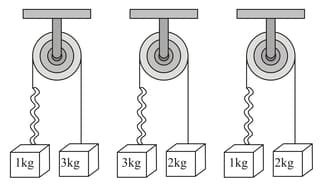
Two blocks of masses and , which are connected with a light string, are placed over a frictionless pulley. This set-up is placed over a weighing machine, as shown. Three combinations of masses and are used. In the first case, and , in second case, and and in the third case, and . The masses are held stationary initially and then released. If the readings of the weighing machine after the release, in three cases, are and , respectively, then,
A block of mass is attached at one end of a light spring and the other end of the spring is connected through a light string to another block of mass , as shown in the figure. is held and is in static equilibrium. Now, is released. The acceleration of just after that instant is . In the next case, is held and is in static equilibrium. Now, when is released, its acceleration immediately after the release is . The value of is (pulley, string and the spring are massless)
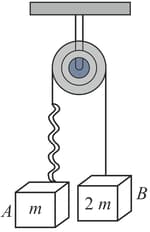
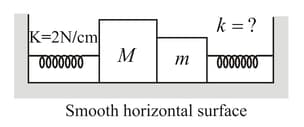
The same spring is attached with , and blocks in three different cases, as shown in the figure. If , and are the extensions in the spring in these cases, then (Assume all the blocks to move with uniform acceleration)
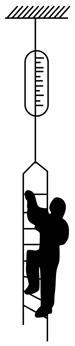
The figure shows a ladder hanging from a string that is connected with the ceiling and is having a spring balance connected in between. A boy of mass is climbing up the ladder at acceleration . Assuming the spring balance and the string to be massless and the spring to show a constant reading, the reading of the spring balance is (Take )
Two blocks of mass and are used to compress two different massless springs, as shown. The left spring is compressed by, while the right spring is compressed by an unknown amount. The system is at rest and all surfaces are fixed and smooth. Which of the following statements are true?