Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Circular Motion, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2 with Hints & Solutions
A particle of mass Is fastened to one end of a string and another one of mass to the middle point; the other end of the string being fastened to a fixed point on a smooth horizontal table. The particles are then projected, so that the two portions of the string are always in the same straight line and describe horizontal circles. Find the ratio of the tensions in the two parts of the string.
A road is wide. Its average radius of curvature is The outer edge is above the lower edge by a distance of . Find the velocity of vehicle for which the road is most suited?
A stone of mass tied to a light string of length is whirling in a circular path in the vertical plane. If the ratio of the maximum to minimum tensions in the string is , find the speeds of the stone at the lowest and highest points.
Calculate the following for the situation shown:-
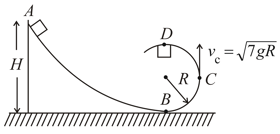
(a) Speed at
(b) Normal reaction at .
(c) Height
A stone weighing tied to a rope of length revolves along a circular path in a vertical plane. The tension of the rope at the bottom point of the circle is . To what height will the stone rise if the rope breaks at the moment when the velocity is directed upwards?
