Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Energy and Respiration, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Mary Jones Biology Solutions for Exercise - Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Energy and Respiration, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Energy and Respiration, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Biology for Cambridge International AS & A Level coursebook 2nd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Energy and Respiration, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
Copy and complete the table to show the respiratory substrates with each of the given RQs.
| Respiratory substrate | RQ |
| _____ | 1.0 |
| _____ | 0.7 |
| _____ | 0.9 |
Measurement of oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide production by germinating seeds in a respirometer showed that 25cm3 of oxygen was used and 17.5 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced over the same time period.
Calculate the RQ for these seeds
Measurement of oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide production by germinating seeds in a respirometer showed that 25cm3 of oxygen was used and 17.5 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced over the same time period.
Identify the respiratory substrate used by the seeds.
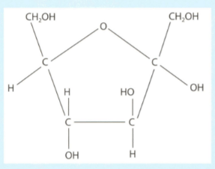
Dahlia plants store a compound called inulin, which is a polymer of fructose. The structure of fructose is shown in the diagram
Calculate the RQ when inulin is hydrolysed and then respired aerobically.
Copy and complete the following passage describing the adaptations of rice for growing with its roots submerged in water.
The stems and roots of rice plants have very large _____ tissue called _____ which allow oxygen to pass from the air to the _____. The roots are very shallow, giving them access to the higher concentration of _____ in surface water. When oxygen concentrations fall, the roots can oxidise glucose through _____. This produces _____, which is toxic. However, the root cells are tolerant of higher concentrations of _____. They also contain high concentrations of enzyme _____ to break it down.
In aerobic respiration, the krebs cycle is regarded as a series of small steps. One of these steps is the conversion of succinate to fumarate by an enzyme, succinate dehydrogenase A.
State the role played by dehydrogenase enzymes in the krebs cycle and explain briefly the importance of this role in the production of ATP.
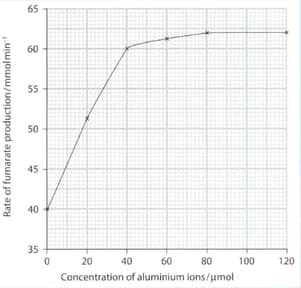
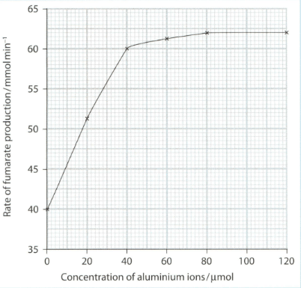
An investigation was carried out into the effect of different concentrations of aluminium ions on the activity of succinate dehydrogenase. The enzyme concentration and all other conditions were kept constant. The graph below shows the results of this investigation.
With reference to the graph, describe the effect of the concentration of aluminium ions on the rate of production of fumarate.
With reference to the graph, suggest an explanation for this effect.