End-of-chapter questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - End-of-chapter questions
Simple step-by-step solutions to End-of-chapter questions questions of The Kinetic Model of Matter from Cambridge IGCSE® Physics Coursebook Second Edition. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from End-of-chapter questions with Hints & Solutions
Boyle's law describes how the volume of a gas depends on its pressure.
Study the following equations. Only three are correct. Select those options which are correct.
A small container of water is placed in an oven at . The water soon disappears. Why must energy be supplied to a liquid to turn it into a gas? In your answer, refer to the particles of the liquid and the forces between them.
A container holds a of air at a pressure of . If the pressure is increased to , what will the volume of the gas become? Assume that its temperature remains constant.
Solids, liquids and gases have different properties. The list below gives some of them.
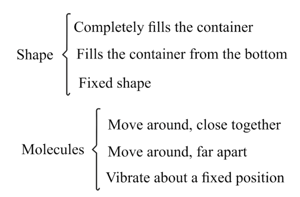
Copy that table and use descriptions from the list to complete it. Any description may be used more than once if appropriate. Two spaces have been filled in to help you.
| Shape | Molecules | ||
| a | Solid | ||
| b | Liquid | Move around, close together | |
| c | Gas | Completely fills the container |
The diagram represents the path taken in air by a smoke particle, as seen in a Brownian motion experiment. The smoke particles can be seen through a microscope, but the air molecules cannot.
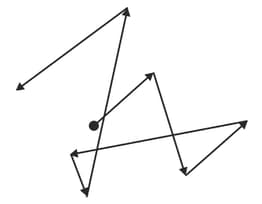
State what causes the smoke particles to move like this.
The diagram represents the path taken in air by a smoke particle, as seen in a Brownian motion experiment. The smoke particles can be seen through a microscope, but the air molecules cannot.

What conclusions about air molecules can be drawn from this observation of the smoke particles?
A can, containing only air, has its lid lightly screwed on and is left in strong sunlight.
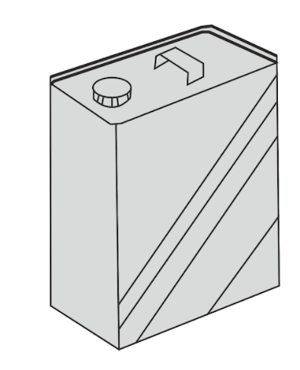
State what happens to the pressure of the air in the can when it gets hot.
A can, containing only air, has its lid lightly screwed on and is left in strong sunlight.
In terms of molecules, explain your answer.
