Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Pathogens and Immunity, Exercise 4: End-of-chapter questions
Mary Jones Biology Solutions for Exercise - Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Pathogens and Immunity, Exercise 4: End-of-chapter questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Pathogens and Immunity, Exercise 4: End-of-chapter questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook Third Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Pathogens and Immunity, Exercise 4: End-of-chapter questions with Hints & Solutions
Copy and complete these sentences.
A microorganism that can make a person ill is called a__________. Some type of bacteria, _________, ___________ and ___________ are pathogens. Some pathogens can get into the body in food and drink. The stomach produces ____________, ___________ which helps to destroy these. The skin has a thick layer of _________ that stops most pathogens getting into it. However, if the skin is cut, pathogens may enter the blood. Blood _________ helps to prevent this. Many of the pathogens that are present in the air that we breathe in are prevented from reaching the lungs, because they are trapped by sticky __________ in the respiratory passages.
Match each of the following term with its description. You need to use one of the term twice.
Active immunity, antibody, antigens, memory, cell, passive immunity, lymphocyte, phagocyte
- Resistance to infection by a particular pathogen, obtained by having the disease or being injected with a weakened pathogen
- Resistance to infection by a particular pathogen, obtained by acquiring antibodies from another organism
- Chemicals on the outer surface of a pathogen that is recognised as foreign by lymphocytes
- A type of white blood cell that ingests and digests bacteria
- A type of white blood cell that produces antibodies
- A long-lived cell produced by the division of activated lymphocytes
- A long-lasting type of immunity
- A protein produced by lymphocytes, which attaches to a specific antigen
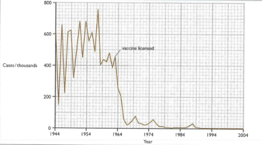
Describe the incidence of measles cases in the USA between and .
Describe the incidence of measles cases in the USA between and .
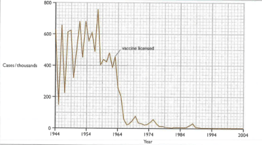
Describe the effect of the introduction of vaccination on the number of measles cases.
Explain why the vaccination of around of population can protect of the population from an infectious disease.
Copy and complete the table to indicate the type of immunity- active or passive, that is obtained by each method.
| Method | Type of immunity |
| Having a disease and recovering from it | |
| Feeding a baby on breast milk | |
| Being injected with antibodies | |
| Receiving a measle's vaccination as a child |
An aid worker is asked to travel immediately to a region where a disaster has taken place. There is a high risk of her being exposed to pathogens that could cause serious diseases. Her doctor recommends that before travelling she should have an injection of antibodies rather than a vaccination of weakened pathogens. Explain the reasons for this.