Aiden Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics and Electric Currents, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Aiden Gill Science Solutions for Exercise - Aiden Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics and Electric Currents, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Electrostatics and Electric Currents, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 9: Workbook solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Aiden Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics and Electric Currents, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
Draw the symbol for an ammeter.
Describe what the current in a circuit represents.
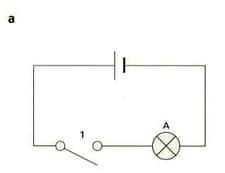
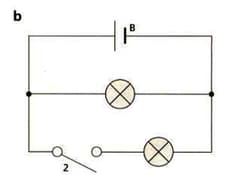
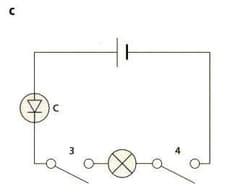
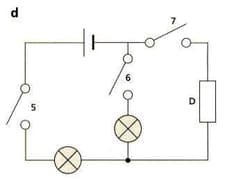
Complete the table that describes the four circuits in the diagrams above.
| Circuit | Series or Parallel | Switches closed to make lamps light | Components |
| a | Series | A = | |
| b | 2 | B = | |
| c | C = | ||
| d | D = resistor |
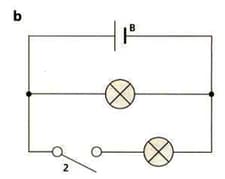
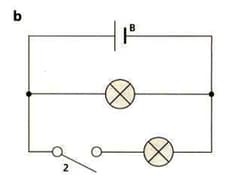
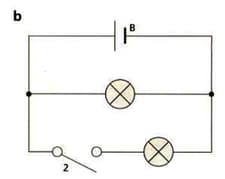
Look at the diagram of circuit b. Yuri reads in a textbook that the current in each branch of a circuit adds up. This would mean that:
Current from the cell = current in upper branch + current in lower branch
What component should Yuri add to the circuit to measure the current?
Look at the diagram of circuit b. Yuri reads in a textbook that the current in each branch of a circuit adds up. This would mean that:
Current from the cell = current in upper branch + current in lower branch
Should this component be connected in series or in parallel.
Look at the diagram of circuit b. Yuri reads in a textbook that the current in each branch of a circuit adds up. This would mean that:
Current from the cell = current in upper branch + current in lower branch
Yuri only has one of these components. Describe how Yuri could use this component to test the statement in the textbook.
The electric circuits in houses include circuit breakers or fuses. These are devices that stop the current if there is a fault.
Describe how a circuit breaker or a fuse can stop a current from flowing.
The electric circuits in houses include circuit breakers or fuses. These are devices that stop the current if there is a fault.
Explain why a circuit breaker or fuse must always be connected in series with the devices connected to a circuit. What could happen if a circuit breaker was connected in parallel with the device that developed a fault?