Objective Problems
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - Objective Problems
Simple step-by-step solutions to Objective Problems questions of Fluid Mechanics from Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 1. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from Objective Problems with Hints & Solutions
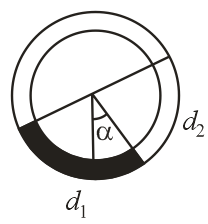
There is a circular tube in a vertical plane. Two liquids which do not mix and of densities and are filled in the tube. Each liquid subtends angle at centre. Radius joining their interface makes an angle with vertical. Ratio is
On heating water, bubbles beings formed at the bottom of the vessel detach and rise. Take the bubbles to be spheres of radius and making a circular contact of radius with the bottom of the vessel. If and the surface tension of water is , value of just before bubbles detach is (density of water is )
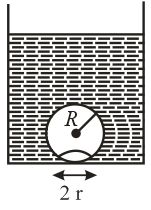
If a ball of steel (density ) attains a terminal velocity of when falling in a tank of water (coefficient of viscosity ) then its terminal velocity in glycerine would be nearly
A large open tank has two holes in its wall. One is a square hole of side at a depth of from the top and the other is a circular hole of radius at a depth from the top. When the tank is completely filled with water, the quantities of water flowing out per second from both holes are the same. Then, is equal to
An object weighs in a liquid of density and that in liquid of density is . The density of the object is
A body floats in water with of its volume outside water. When the same body floats in an oil, of its volume remains outside oil. The relative density of oil is
A ball is made of a material of density , where with and representing the densities of oil and water respectively. The oil and water are immiscible. If the above ball is in equilibrium in a mixture of this oil and water, which of the following pictures represents its equilibrium position?
Three liquids of equal masses are taken in three identical cubical vessels and . Their densities are and respectively but . The force exerted by the liquid on the base of the cubical vessel is
