D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 14: Objective Problems [Level 1]
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 14: Objective Problems [Level 1]
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: Geometric Optics, Exercise 14: Objective Problems [Level 1] with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 2 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 14: Objective Problems [Level 1] with Hints & Solutions
Which of the following can form a virtual, erect and magnified image?
Match List I (Phenomenon) with List II (Principle) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
| List I | List II | ||
| (I) | Blue colour of a sky | (A) | Total internal reflection |
| (II) | Glittering of diamond | (B) | Dispersion of light |
| (III) | Formation of rainbow | (C) | Scattering of light |
| (IV) | In the evening when the sun goes down below the horizon, it continues to remain visible for some time | (D) | Refraction of light |
A convex and a concave mirror of radii each are placed facing each other and apart. An object is placed exactly between them. If the reflection first takes place in concave and then in convex mirror, the position of the final image will be
When the bodies placed in a dark room are exposed to -rays, they appear
The work of Prof. Raman for which he was awarded Nobel Prize was concerned with
A double convex glass lens having focal length equal to the focal length of a concave mirror. The radius of curvature of the concave mirror is
Rainbow is observed when the sun is
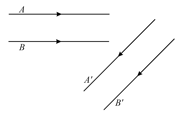
Figure shows two rays and being reflected by a mirror and going as and . The mirror