D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 15: Objective Problems [Level 2]
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 15: Objective Problems [Level 2]
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: Geometric Optics, Exercise 15: Objective Problems [Level 2] with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 2 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Geometric Optics, Exercise 15: Objective Problems [Level 2] with Hints & Solutions
A biconvex lens of focal length is in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the lens and the mirror is . A small object is kept at a distance of from the lens. The final image is,
The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is . When an object is moved from a distance of in front of it to , the magnification of its image changes from to . The ratio is,
A square wire of side is placed perpendicular to the principle axis of a concave mirror of focal length at a distance of . The area enclosed by the image of the wire is,
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of . The angle of deviation produced by the mirror is,
A point object is placed in front of a glass rod having spherical end of radius of curvature . The image would be formed,
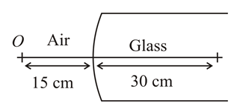
and are the parallel sided transparent media of refractive indices and , respectively. They are arranged as shown in the figure. A ray is incident at an angle on the surface of separation of and as shown in the figure. After refraction in the medium , the ray grazes the surface of separation of the media and . Then, is equal to,
A boat has green light of wavelength, on the mast. What wavelength would be measured and what colour would be observed for this light as seen by a diver submerged in water by the side of the boat? Given, .
Two beams of red and violet colours are made to pass separately through a prism of . In the minimum deviation position, the angle of refraction inside the prism will be,
