David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Questions
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 13: Light, Exercise 3: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE® Physics Coursebook Second Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Questions with Hints & Solutions
Look at the table. What is the value of the refractive index of a diamond?
The figure shows what happens when a ray of light enters blocks of two different materials, A and B
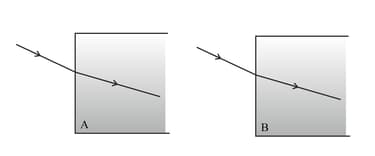
(a) In which material does the light travel more slowly, A and B? Explain how you can tell from the diagrams.
(b) Which material, A or B, has the greater refractive index?
Light travels more quickly through water than through glass. Which has the greater refractive index, water or glass?
Light travels more quickly through water than through glass. If a ray passes from glass into water, which way will it bend: towards or away from the normal?
The speed of light in a block of glass is found to be . Calculate the refractive index of the glass. (The speed of light in a vacuum is )
A solution of sugar in water is found to have a refractive index of . Calculate the speed of light in the solution. (The speed of light in vacuum is )
Perspex is a form of transparent plastic. It has a refractive index . A ray of light strikes the flat surface of a Perspex block with an angle of incidence of . What will be the angle of refraction?

