David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Motion, Exercise 8: End-of-chapter questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Motion, Exercise 8: End-of-chapter questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 3: Forces and Motion, Exercise 8: End-of-chapter questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE® Physics Coursebook Second Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Motion, Exercise 8: End-of-chapter questions with Hints & Solutions
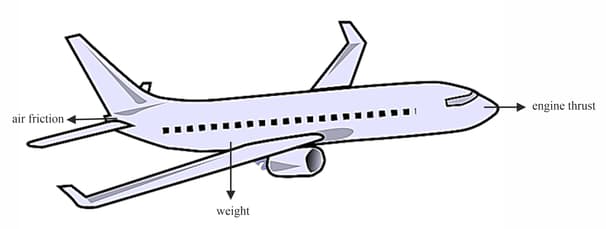
An aeroplane is flying horizontally at a steady speed in a straight line. The diagram shows three of the four forces acting on it.
In order to fly horizontally at a steady speed, which two of the forces shown on the aeroplane must be equal?
An aeroplane is flying horizontally at a steady speed in a straight line. The diagram shows three of the four forces acting on it.
in order to fly horizontally in a straight line, there must be a fourth force acting on the plane. Draw an arrow to represent this force.
The aeroplane flies an outward journey from Budapest (Hungary) to Palermo (Italy) in The distance is Calculate, the average speed of aeroplane.
The aeroplane flies an outward journey from Budapest (Hungary) to Palermo (Italy) in . The distance is On the return journey from Palermo to Budapest, the journey time is shorter, even though the engine thrust is the same. Suggest what might have caused the return journey to be shorter.
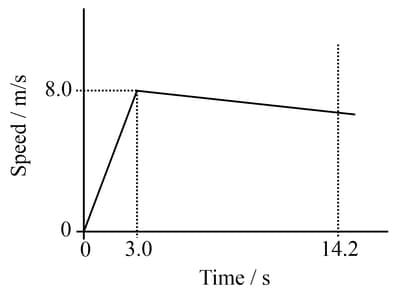
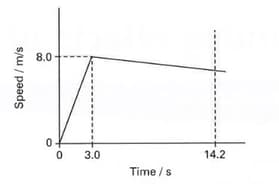
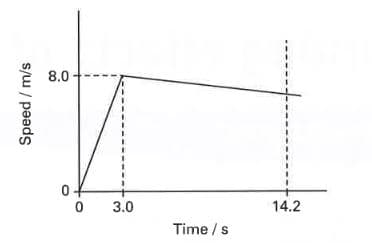
A young athlete has a mass of . On a day when there is no wind, she runs race in . A sketch graph showing her speed during the race is.
The acceleration of the athlete during the first of the race.
A young athlete has a mass of . On a day when there is no wind, she runs a race in . A sketch graph showing her speed during the race is given below. The accelerating force on the athlete during the first of the race is:
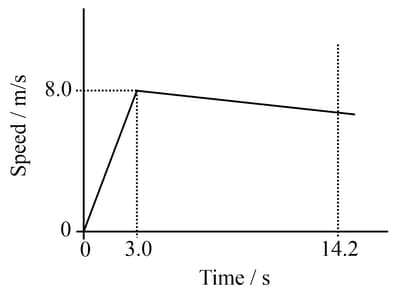
A young athlete has a mass of . On a day when there is no wind, she runs a race in . A sketch graph showing her speed during the race is given.
Find the speed with which she crosses the finishing line.
A young athlete has a mass of . On a day when there is no wind, she runs a race in . A sketch graph showing her speed during the race is given.
Suggest two difference that might be seen in the graph if there had been a strong wind opposing the runners in the race.