David Sang and Darrell Hamilton Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Circuits, Exercise 4: Exercise 19.4
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Darrell Hamilton Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Circuits, Exercise 4: Exercise 19.4
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 19: Electrical Circuits, Exercise 4: Exercise 19.4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge IGCSE workbook solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Darrell Hamilton Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Circuits, Exercise 4: Exercise 19.4 with Hints & Solutions
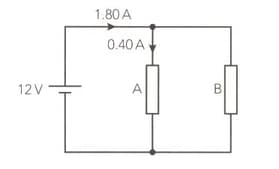
Current flowing through the resistor is Calculate the potential difference of the battery?
The resistors A and B are connected in parallel to a . The current flowing through the battery and resistor A is marked in the diagram.
Calculate the resistance of resistor A (in ohms)?
Explain the benefits of wiring devices in parallel.
The resistors A and B are connected in parallel to a . The current flowing through the battery and resistor A is marked in the diagram.
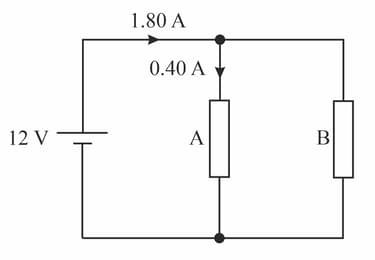
Calculate the current through resistor B and explain your answer ?
The resistors A and B are connected in parallel to a . The current flowing through the battery and resistor A is marked in the diagram.
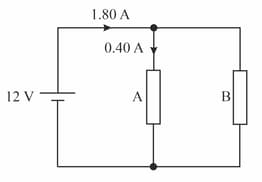
Calculate the resistance of resistor B (in ohms)?
A solar current is required to produce the same current throughout its operation. The potential difference across it varies with light level. State what must change in the circuit, to ensure that the current remains constant as the potential difference rises.
The resistors A and B are connected in parallel to a battery. The current flowing through the battery and resistor A is marked in the diagram.
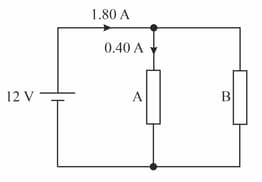
Calculate the combined resistance of A and B? Given
Two cells of emf are connected in series with a resistor . The current flowing is . One of the cells is now reversed . The current flowing is . Calculate the ratio of .