David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism, Exercise 10: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism, Exercise 10: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 24: Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism, Exercise 10: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism, Exercise 10: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
At a certain point on the Earth's surface, the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is A piece of wire long and weight lies in an east- west direction on a laboratory bench. When a large current flows in the wire, the wire just lifts off the surface of the bench. Calculate the minimum current needed to lift the wire
from the bench.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
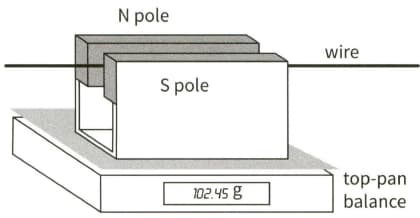
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(a) Explain why the reading on the top-pan balance decreases
when the current is switched on.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
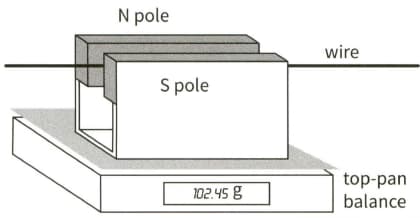
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(b) State and explain the direction of the current flow in the wire.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
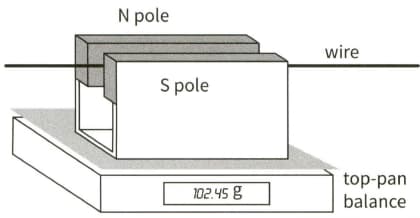
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(c) The length of the wire in the magnetic field is Calculate the average magnetic flux density between the poles of the magnet.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
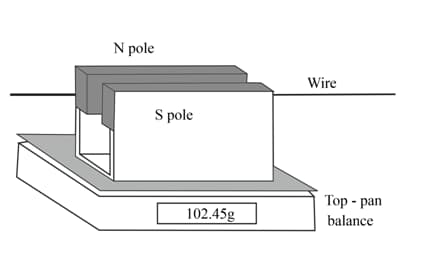
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(d) Sketch a graph, with balance reading on the vertical axis and current on the horizontal axis, to show how the balance reading changes when the current is altered.
(a) Define magnetic flux density and explain the similarity with the definition of electric field strength.
(b) Two thin horizontal wires are placed in a north- south direction. One wire is placed on a bench and the other wire is held directly above the first wire.
(i) When equal currents flow in the two wires, the force exerted on the bench by the lower wire decreases. Explain why this is so. What can you say about the directions of the currents in the two wires?
Two thin horizontal wires are placed in a north- south direction. One wire is placed on a bench and the other wire is held Directly above the first wire.
The magnetic flux density Bat a distance x from a long straight wire carrying a current i is given by the expression Where X is in metres and i is in ampere. When the current in each wire is Calculate the force per unit length on one wire due to the current in the other.
