David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 8: Questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 8: Questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Matter and Materials, Exercise 8: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 8: Questions with Hints & Solutions
List the metals in Table from stiffest to least stiff.
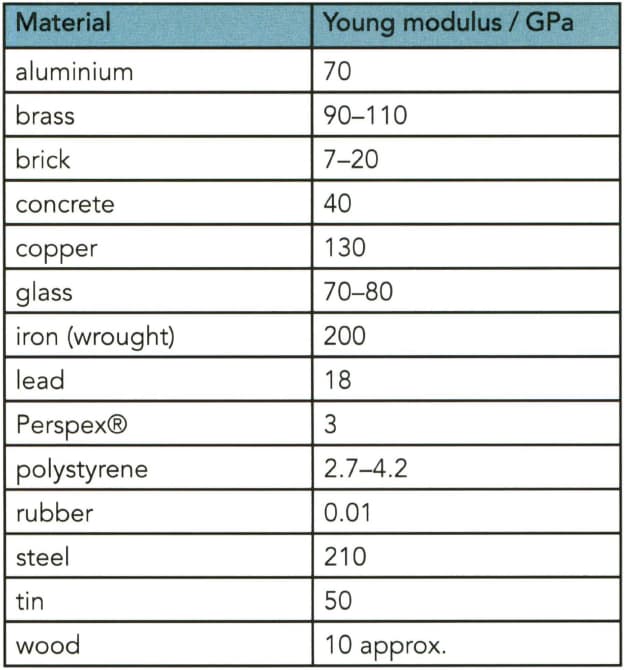
The Young modulus of various materials. Many of these values depend on the precise composition of the material concerned.
Which of the non-metals in Table is the stiffest?
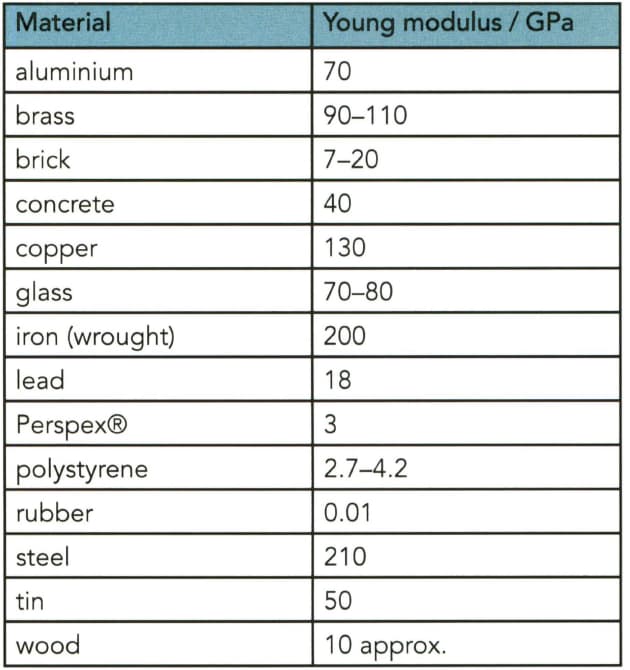
The Young modulus of various materials. Many of these values depend on the precise composition of the material concerned.
Figure shows stress- strain graphs for two materials, A and B. Use the graphs to determine the Young modulus of each material.
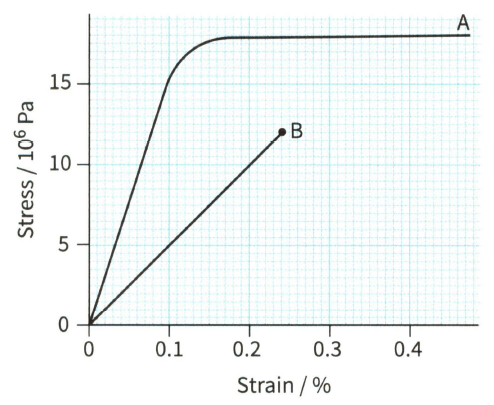
Stress-strain graphs for two different materials.
A piece of steel wire, long and having cross-sectional area of , is stretched by a force of . Its new length is found to be . Calculate the stress and strain, and the Young modulus of steel.
Calculate the extension of a copper wire of length and diameter when a tensile force of is applied to the end of the wire. (Young modulus of copper )
In an experiment to measure the Young modulus of glass, a student draws out a glass rod to form a fibre in length. Using a travelling microscope, she estimates its diameter to be . Unfortunately, it proves impossible to obtain a series of readings for load and extension. The fibre snaps when a load of is hung on the end. The student judges that the fibre extended by no more than before it snapped. Use these values to obtain an estimate for the Young modulus of the glass used. Explain how the actual or accepted value for the Young modulus might differ from this estimate.
For each of the materials whose stress-strain graphs are shown in Figure, deduce the values of the Young modulus.
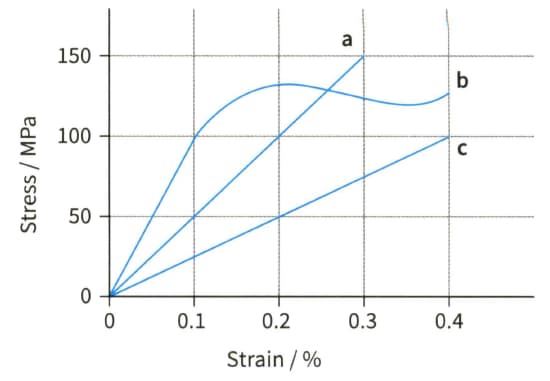
Stress-strain graphs for three materials.
