Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 4: EXERCISE 4C
Dean Chalmers Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 4: EXERCISE 4C
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Probability, Exercise 4: EXERCISE 4C with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics : Probability & Statistics 1 Course Book solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 4: EXERCISE 4C with Hints & Solutions
A coin is biased such that the probability that three tosses all result in heads is . Find the probability of obtaining no heads with three tosses of the coin.
In a group of five men and four women, there are three pairs of male and female business partners and three teachers, where no teacher is in a business partnership. One man and one woman are selected at random. Find the probability that they are:
both teachers
In a group of five men and four women, there are three pairs of male and female business partners and three teachers, where no teacher is in a business partnership. One man and one woman are selected at random. Find the probability that they are:
in a business partnership with each other
In a group of five men and four women, there are three pairs of male and female business partners and three teachers, where no teacher is in a business partnership. One man and one woman are selected at random. Find the probability that they are:
each in a business partnership but not with each other.
A game board is shown in the diagram.
Players take turns to roll an ordinary fair die, then move their counters forward from 'start' a number of squares equal to the number rolled with the die. If a player's counter ends its move on a coloured square, then it is moved back to the start.
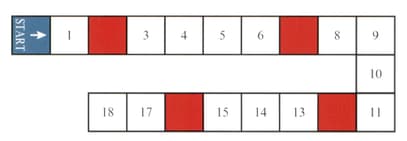
Find the probability that a player's counter is on 'start' after rolling the die once.
A game board is shown in the diagram.
Players take turns to roll an ordinary fair die, then move their counters forward from 'start' a number of squares equal to the number rolled with the die. If a player's counter ends its move on a coloured square, then it is moved back to the start.
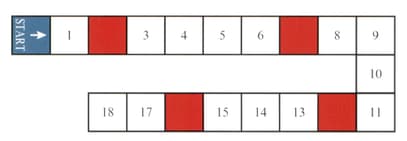
Find the probability that a player's counter is on 'start' after rolling the die twice.
A game board is shown in the diagram.
Players take turns to roll an ordinary fair die, then move their counters forward from 'start' a number of squares equal to the number rolled with the die. If a player's counter ends its move on a coloured square, then it is moved back to the start.
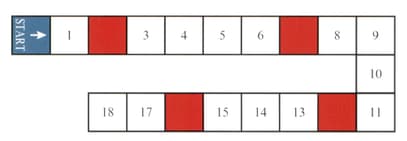
Find the probability that after rolling the die three times, a player's counter is on .
A game board is shown in the diagram.
Players take turns to roll an ordinary fair die, then move their counters forward from 'start' a number of squares equal to the number rolled with the die. If a player's counter ends its move on a coloured square, then it is moved back to the start.
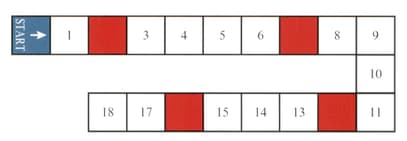
Find the probability that after rolling the die three times, a player's counter is on .
