Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 1: Meghalaya-2018
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 1: Meghalaya-2018
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 1: Meghalaya-2018 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 1: Meghalaya-2018 with Hints & Solutions
Calculate the force per unit length between two parallel long straight wires apart in air, each carrying a current of .
Using Biot-Savart law, find an expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a circular current-carrying loop. Hence, find the expression for the magnetic field at its centre.
To convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter, we must connect a
Two parallel wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other while two beams of electrons travelling in the same direction repel each other. Explain why.
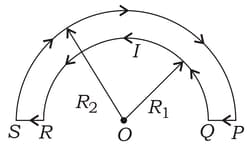
The wire loop formed by joining two semi-circular wires of radii and carries a current as shown in the figure below. Find the magnitude of magnetic field at .
Describe the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer and hence show that the deflection of the coil is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. What is the effect of the radial magnetic field in a moving coil galvanometer?
With the help of a labeled diagram, state the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Explain clearly how it works to accelerate the charged particles. Is there an upper limit on the energy acquired by the particle? Given reason.
Derive the torque on a rectangular current-carrying loop placed in a uniform magnetic field. Draw suitable figures. Write one application of this principle.
