Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
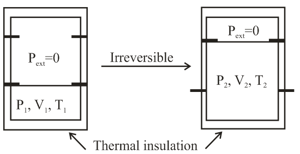
An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure volume and absolute temperature expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of the gas are and , respectively. For this expansion
A piston filled with mol of an ideal gas expands reversibly from to at a constant temperature of As it does so, it absorbs of heat. The values of and for the process will be:
equal to:
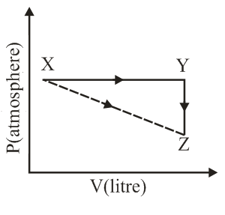
For an ideal gas, consider only work in going from an initial state to the final state The final state can be reached by either of the two paths shown in the figure. Which of the following choice is (are) correct? [take as change in entropy and w as work done].
Identify the CORRECT statement regarding a spontaneous process.
In conversion of lime-stone to lime, the values and are and respectively at and . Assuming that and do not change with temperature, temperature above which conversion of lime stone to lime will be spontaneous is :
The heats of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are and respectively. The heat of formation (in ) of carbon monoxide per mole is :
The value of for a reaction is
(Given and )
