Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
A stationary body explodes into four identical fragments such that three of them fly off mutually perpendicular to each other, each with the same The minimum energy of explosion will be,
Three identical balls of mass m and radius are placed on frictionless horizontal Ball at Ball at Ball is suddenly given an impulse If collision between balls is perfectly elastic while between is head on and perfectly inelastic, then.
A projectile is thrown horizontally from top of a tower of heightwith a velocity It strikes the smooth ground whose co-efficient of restitution is (neglect friction):
Two ballsmoving in the same direction collide. The mass of is times that of Before the collision the velocity of was times that of After the collision comes to rest. If be the coefficient of restitution then which of the following conclusion/s is/are correct ?
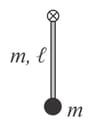
A particle is attached to the lower end of a uniform rod which is hinged at its other end as shown in the figure. The minimum speed given to the particle so that the rod performs circular motion in a vertical plane will be [length of the rod is , consider masses of both rod and particle to be same]
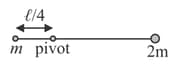
A rod of negligible mass and length is pivoted at the point distance from the left end as shown. A particle of mass is fixed to its left end and another particle of mass is fixed to the right end. If the system is released from rest and after some time becomes vertical, the speed of the two masses and angular velocity at that instant is
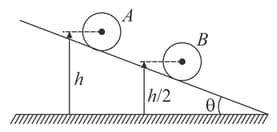
Two identical balls and of mass each is placed on a fixed wedge as shown in the figure. The ball is kept at rest and it is released just before two balls collide. The ball rolls down without slipping on an inclined plane and collides elastically with the ball . The kinetic energy of the ball just after the collision with the ball is (Neglect friction between and , also neglect the radius of the balls)
Consider two point masses and connected by a light rigid rod of length . The moment of inertia of the system about an axis passing through their centre of mass and perpendicular to the rigid rod is given by
