Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise - 3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise - 3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 16: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise - 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise - 3 with Hints & Solutions
Two spherical bodies (radius ) and (radius ) are at temperatures and , respectively. The maximum intensity in the emission spectrum of is at and in that of is at . Considering them to be black bodies, what will be the ratio of the rate of total energy radiated by to that of ?
The temperature of the middle (i.e. second) plate under steady state condition, when three very large plates of same area are kept parallel and close to each other. They are considered as ideal black surfaces and have very high thermal conductivity. The first and third plates are maintained at temperatures and respectively.
Parallel rays of light of intensity, are incident on a spherical blackbody kept in surroundings of temperature . Take Stefan-Boltzmann's constant, and assume that the energy exchange with the surroundings is only through radiation. The final steady-state temperature of the blackbody is close to,
If a piece of metal is heated to temperature and then allowed cooling in a room which is at temperature , the graph between the temperature of the metal and time t will be closest to
Find Rate of flow of heat through copper rod, where three rods of copper, Brass and steel are welded together to form a -shaped structure. Area of cross-section of each rod. End of copper rod is maintained at whereas ends of brass and steel are kept at . Lengths of copper, brass and steel rods are and respectively. The rods are thermally insulated from surroundings except at ends. The thermal conductivities of copper, brass and steel are and units respectively.
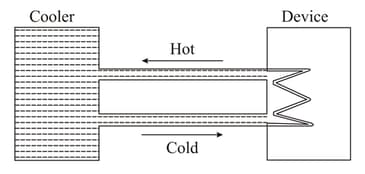
A water cooler of storage capacity can cool water at a constant rate of . In a closed circulation system (as shown schematically in the figure), the water from the cooler is used to cool an external device that generates constantly of heat (thermal load). The temperature of water fed into the device cannot exceed and the entire stored of water is initially cooled to . The entire system is thermally insulated. The minimum value of (in ) for which the device can be operated for is
The ends and of two thin wires, and are soldered (joined) together. Initially, each of the wire has a length of at . Now, the end is maintained at while the end is heated and maintained at The system is thermally insulated from its surroundings. If the thermal conductivity of wire is twice that of the wire and the coefficient of linear thermal expansion of is , the change in length of the wire is
Time taken by a heater to heat one litre of water from to is: (specific heat of water is )
