Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Simple Harmonic Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Simple Harmonic Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 19: Simple Harmonic Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Simple Harmonic Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
The oscillation of a body on a smooth horizontal surface is represented by the equation, , where displacement at time , frequency of oscillation. Which one of the following graph shows correctly the variation with ?
Here, acceleration at time ,
time period.
A particle moves with simple harmonic motion in a straight line. In first after starting from rest it travels a distance and in the next it travels in the same direction, then
For a simple pendulum, a graph is plotted between its kinetic energy and potential energy against its displacement . Which one of the following represents these correctly? (The graphs are schematic and not drawn to scale)
A particle performs simple harmonic motion with amplitude . Its speed is trebled at the instant that it is at distance from equilibrium position. The new amplitude of the motion is
A particle is executing simple harmonic motion with a time period . At time , it is at its position of equilibrium. The kinetic energy-time graph of the particle will look like :
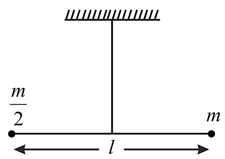
Two masses and are connected at the two ends of a massless rigid rod of length . The rod is suspended by a thin wire of torsional constant at the centre of mass of the rod-mass system (see figure). Because of torsional constantthe restoring torque is . for angular displacement If the rod is rotated by and released, the tension in it when it passes through its mean position will be :
A wooden cube (density of wood ) of side floats in a liquid of density with its upper and lower surfaces horizontal. If the cube is pushed slightly down and released, it performs a simple harmonic motion of period . Then, is equal to:
A cylindrical plastic bottle of negligible mass is filled with of water and left floating in a pond with still water. If pressed downward slightly and released, it starts performing simple harmonic motion at angular frequency, . If the radius of the bottle is then is close to (density of water )
