Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties, Exercise 3: Level 3
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties, Exercise 3: Level 3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties, Exercise 3: Level 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties, Exercise 3: Level 3 with Hints & Solutions
The correct order of Pauling electronegativity is:
Among the elements and , Which would show the greatest difference in first and second ionisation enthalpies?
Select equations having exothermic step:
How many of the following have greater than Silicon atom:
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix)
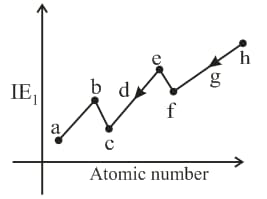
Where are period elements. If the difference between the atomic numbers of elements and is and the difference between the atomic number of elements and is What is the value of
The electron gain enthalpy of a hypothetical element is per atom. How much energy in is released when of are completely converted to , ions in gaseous state ? (Molar mass of )
Find the total number of cations for which of cation is lower than corresponding atom.
According to Slater effective nuclear charge, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge of the nucleus of the atom. depends on the type of orbital In which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons
in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is The effective nuclear charge due to screening is given by where is the atomic number and is the slater screening constant values:
| Electrons in orbitals |
per electron in orbital | ||
| etc. | |||
| or orbital | |||
| or orbital | |||
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbital, is not considered in calculation of
What is for
