Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Structure of Atom, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2013
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Structure of Atom, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2013
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Structure of Atom, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2013 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR CHEMISTRY solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Structure of Atom, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2013 with Hints & Solutions
Consider a helium atom that absorbs a photon of wavelength . The change in the velocity (in ) of atom after the photon absorption is ______.
(Assume: Momentum is conserved when a photon is absorbed.
Use: Planck constant , Avocados number , Molar mass of )
Give your answer as the nearest integer.
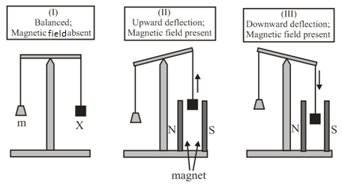
In an experiment, grams of a compound (gas/liquid/solid) taken in a container is loaded in a balance as shown in figure below. In the presence of a magnetic field, the pan with is either deflected upwards (figure ), or deflected downwards (figure ), depending on the compound . Identify the correct statement(s).
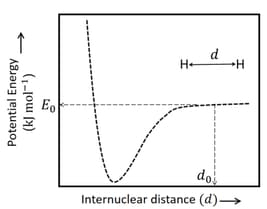
The figure below is the plot of potential energy versus internuclear distance of molecule in the electronic ground state. The value of the net potential energy (as indicated in the figure) is for at which the electron-electron repulsion and the nucleus-nucleus repulsion energies are absent, find the value of to the nearest integer value.
As reference, the potential energy of atom is taken as zero when its electron and the nucleus are infinitely far apart.
Use Avogadro constant as Give an answer to the nearest integer value.
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is . Consider an electronic state of whose energy, azimuthal quantum number and magnetic quantum number are and respectively. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true for the state ?
Consider the Bohr's model of a one-electron atom where the electron moves around the nucleus. In the following List-I contains some quantities for the orbit of the atom and List-II contains options showing how they depend on .
| List - I | List - II |
|---|---|
| (I) Radius of the orbit | |
| (II) Angular momentum of the electron in the orbit | |
| (III) Kinetic energy of the electron in the orbit | |
| (IV) Potential energy of the electron in the orbit | |
Which of the following options has the correct combination considering List-I and List-II?
Consider the Bohr's model of a one-electron atom where the electron moves around the nucleus. In the following List-I contains some quantities for the orbit of the atom and List-II contains options showing how they depend on .
| List - I | List - II |
|---|---|
| (I) Radius of the orbit | |
| (II) Angular momentum of the electron in the orbit | |
| (III) Kinetic energy of the electron in the orbit | |
| (IV) Potential energy of the electron in the orbit | |
Which of the following options has the correct combination considering List-I and List-II?
Among the species given below, the total number of diamagnetic species is ___.
(superoxide), dimeric sulphur in vapour phase,
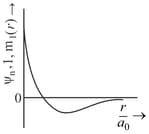
The wave function, is a mathematical function whose value depends upon spherical polar coordinates of the electron and characterized by the quantum numbers and . Here is the distance from the nucleus, is colatitude and is azimuth. In the mathematical functions given in the Table, is the atomic number and is Bohr radius
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
| (I) orbital | (i) |
(P) |
| (II) orbital | (ii) One radial node | (Q) Probability density at the nucleus . |
| (III) orbital | (iii) | (R) Probability density is maximum at the nucleus. |
| (IV) orbital | (iv) -plane is a nodal plane | (S) Energy needed to excite an electron from state to state is times the energy needed to excite are electron from state to state. |