Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 1: KEAM 2020
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 1: KEAM 2020
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 1: KEAM 2020 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 1: KEAM 2020 with Hints & Solutions
The radius of gyration about an axis through the center of a hollow sphere with external radius and internal radius is
A hollow sphere and a solid sphere, of equal mass and equal radii roll down without slipping on an inclined plane, If the torque experienced by the hollow sphere and solid sphere are and respectively, then
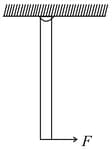
A uniform bar of mass is supported by a pivot at its top about which the bar can swing like a pendulum. If a force is applied perpendicular to the lower end of the bar as shown in figure, what is the value of in order to hold the bar in equilibrium at an angle from the vertical
A solid sphere of radius is revolving about one of its diameters with an angular velocity If it suddenly expands uniformly so that its radius increases to times its original value, then its angular velocity becomes
A thin circular ring of mass and radius is rotating about its axis perpendicular to the plane of the ring with a constant angular velocity . Two point particles each of mass are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates, with an angular velocity . Then, the ratio is
If a ring rolls down from top to bottom of an inclined plane, it takes time If it slides, it takes time Then the ratio is
A ball of mass and radius starting from test rolls down on a inclined plane. The torque acting on the ball at the distance of the from the starting point is close to (take acceleration due to gravity as
If the radius of the earth suddenly decreases by half of its present value. Then the time duration of one day will be
