Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014 with Hints & Solutions
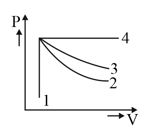
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state as shown in the figure below. Those processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. The curve which represents the adiabatic process among and is:
The efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon
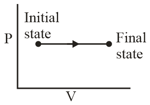
The diagram for an ideal gas in a piston cylinder assembly undergoing a thermodynamic process is shown in the figure. The process is
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stop cock. A contains an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stop cock is suddenly opened. The process is:
In which of the following processes, heat is neither absorbed nor released by a system?
A sample of of water at and normal pressure requires of heat energy to convert to steam at . If the volume of the steam produced is the change in internal energy of the sample, is
A monoatomic gas at a pressure having a volume expands isothermally to a volume and then adiabatically to a volume The final pressure of the gas is: (take )
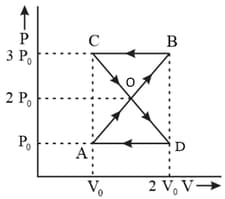
A thermodynamics system undergoes cyclic process as shown in Figure. The work done by the system in the cycle is: