Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course (Based on Revised Syllabus-2023) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
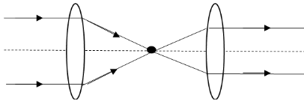
Ray diagram for two lenses kept at some distance given in the diagram, which of the following option is correct (f1,f2=focal length; d=distance between lenses)
The refractive index of material of a Plano-convex lens, if the radius of curvature of the plane surface is infinite while the radius of curvature of convex surface is and focal length of the lens is , will be:
A biconvex lens made of glass (refractive index ) has two spherical surfaces having radii and . Calculate its focal length.
A concave lens of focal length product an image half in size of the real object. The distance of the real object is
Is magnification positive for concave lens?
For two thin lenses kept in contact with each other, show that:
where the terms have their usual meaning.
How is focal length defined for a two lens system, separated by distance d?
When two thin lenses are kept in contact, prove that their combined or effective focal length F is given by:
where the terms have their usual meaning.