Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise#1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise#1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 1: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise#1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SX Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatics, Exercise 1: Exercise#1 with Hints & Solutions
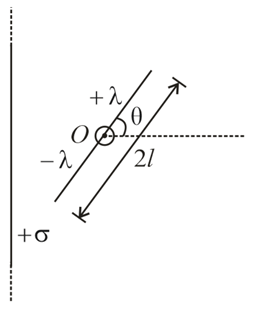
A large sheet carries uniform surface charge density A rod of length , has a linear charge density , on one half and , on the second half. The rod is hinged at mid-point , and makes angle , with the normal to the sheet. The electric force experienced by the rod is
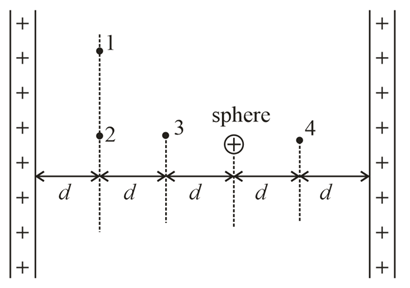
The figure shows two large, closely placed, parallel, nonconducting sheets with identical (positive) uniform surface charge densities, and a sphere with a uniform (positive) volume charge density. Four points marked as and are shown in the space in between. If and are the magnitude of net electric fields at these points respectively then:
Two similar very small conducting spheres having charges and are some distance apart. Now they are touched and kept at the same distance. The ratio of the initial to the final force between them is:
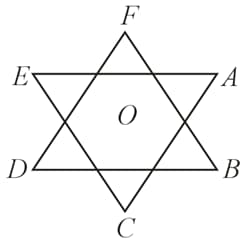
The magnitude of the electric force on charge placed at the center of two equilateral triangles each of side as shown in the figure is If charge and are , respectively, then the value of is:
There is a uniform electric field in -direction. If the work done by external agent in moving a charge of through a distance of slowly along the line making an angle of with -direction is , then the magnitude of is:
Two equal positive charges are kept at points and The electric potential, while moving from to along straight line:
A semicircular ring of radius is uniformly charged with a total charge of . The electric potential at the center of this ring is:
A charge experiences a constant force of , when moved between two points separated by a distance of in a uniform electric field. The potential difference between these two points is:
