Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 3: EXERCISE 6.3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 3: EXERCISE 6.3
Attempt the practice questions from Exercise 3: EXERCISE 6.3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 3: EXERCISE 6.3 with Hints & Solutions
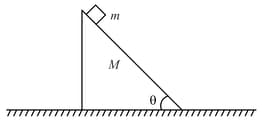
The block wedge system shown in the figure is released from rest. All the surfaces are smooth. Find the speed of the wedge when the speed of the block w.r.t. wedge is .
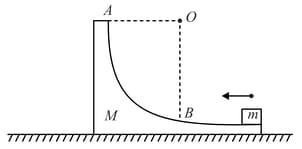
A block of mass is moving with speed on a wedge of mass which is placed upon a horizontal surface. Track is a circular track of radius . What is the minimum speed , so that the block reaches point (All surfaces are frictionless)?
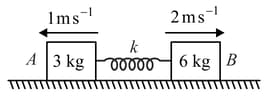
Two blocks and are connected by a spring of stiffness and placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Initially the spring has its equilibrium length. The indicated velocities are imparted to and . The maximum extension of the spring will be
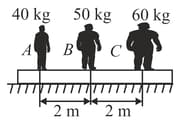
Three men and of masses and are standing on a plank of mass , which is kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If and exchange their positions then mass will shift
A bead can slide on a smooth straight wire and a particle of mass attached to the bead by a light string of length . The particle is held in contact with the wire and with the string taut and is then let fall. If the bead has mass then when the string makes an angle with the wire, the bead will have slipped a distance
A trolley (Having man) was moving horizontally on a smooth ground with velocity with respect to earth. Suddenly man starts running from rear end of the trolley with a velocity . After reaching the other end, the man turns back and continues running with same the velocity of with respect to trolley in opposite direction. If the length of trolley is , find the displacement of the man with respect to earth when he reaches the starting point on the trolley. [Mass of trolley is equal to the mass of the man.]
A wagon of can move without friction along horizontal rails. A simple pendulum consisting of a sphere of mass is suspended from the ceiling of the wagon by a string of length . At the initial moment the wagon and the pendulum are at rest and the string is deflected through an angle from the vertical. Find the velocity of the wagon when the pendulum passes through the mean position.
