H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: EXERCISES
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of and at full speed. Consider a particle of mass sticking at the outer end of a blade.
(a) How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed?
(b) Who exerts this force on the particle?
(c) How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass is . Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator.
(a) By what fraction is the balance reading less than his true weight?
(b) If the speed of Earth's rotation is increased by such an amount that the balance reading is half the true weight, what will be the length of the day in this case?
A turn of radius is banked for the vehicles going at a speed of . If the coefficient of static friction between the road and the tyre is , what are the possible speeds of a vehicle, so that it neither slips down nor skids up?
A motorcycle has to move with a constant speed on an overbridge which is in the form of a circular arc of radius and has a total length . Suppose the motorcycle starts from the highest point.
(a) What can its maximum velocity be for which the contact with the road is not broken at the highest point?
(b) If the motorcycle goes at speed times the maximum found in part where will it lose the contact with the road?
(c) What maximum uniform speed can it maintain on the bridge if it does not lose contact anywhere on the bridge?
A car goes on a horizontal circular road of radius the speed increasing at a constant rate The friction coefficient between the road and the tyre is Find the speed at which the car will skid.
A block of mass is kept on a horizontal ruler. The friction coefficient between the ruler and the block is The ruler is fixed at one end and the block is at a distance from the fixed end. The ruler is rotated about the fixed end in the horizontal plane through the fixed end.
(a) What can the maximum angular speed be for which the block does not slip?
(b) If the angular speed of the ruler is uniformly increased from zero at an angular acceleration at what angular speed will the block slip?
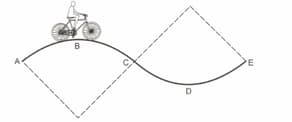
A track consists of two circular parts and of equal radii , and joined smoothly, as shown in the figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing together with the rider travels at a constant speed of on the track.
(a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle, when it is at and at .
(b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres, when the cycle is at .
(c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle, just before and just after the cycle crosses .
(d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take .