H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 18: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II with Hints & Solutions
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
Mark the correct options.
Which of the following (with reference to a spherical mirror) do (does) not depend on whether the rays are paraxial or not?
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
A convex lens forms a real image of a point object placed on its principal axis. If the upper half of the lens is painted black,
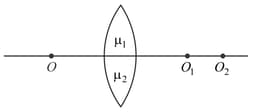
Consider three converging lenses and having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of and are and , respectively. The upper half of the lens has a refractive index and the lower half has . A point object imaged at by the lens and at by the lens placed in same position. If, is placed at the same place,
A screen is placed at a distance away from an illuminated object. A converging lens is placed between the source and the screen and it is attempted to form the image of the source on the screen. If no position could be found, the focal length of the lens
