Heena Sharma, Shubhankat Vats and, Rashmi Gupta Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 6: Challengers*
Heena Sharma Science Solutions for Exercise - Heena Sharma, Shubhankat Vats and, Rashmi Gupta Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 6: Challengers*
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 11: Work and Energy, Exercise 6: Challengers* with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. All In One SCIENCE CBSE Class IX solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Heena Sharma, Shubhankat Vats and, Rashmi Gupta Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 6: Challengers* with Hints & Solutions
The energy absorbed by a solar panel is used to charge a battery. During the day, the battery storesof energy each second. At night the battery is used to light a lamp for What is the minimum time for which the battery must be charged within the day?
A force of acts on a body initially at rest. The work done by the force during the first second of motion of the body is
A force is applied by an engine of a train of mass changes its velocity from. Power of engine is
Natural length of a spring is and its spring constant is A mass of is hung from it. The extension produced in the spring is, (take,)
A lorry and a car moving with the same K E are brought to rest by applying the same retarding force, then;
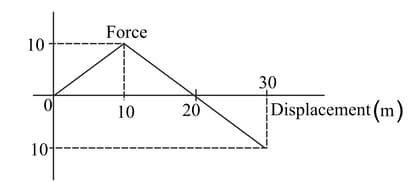
The figure shows the variation of force and displacement. Find the value of work done at the end of the displacement is
Water falls from a height of at the rate of to operate a turbine. The losses due to frictional forces are of energy. How much power is generated by the turbine? (take,)
A block mass of is dropped from a height of from the earth's surface and it falls onto a vertical helical spring of stiffness and length . The compression of the spring is (Take )